LangGraph 공식문서를 번역한 내용입니다. 필요한 경우 부연 설명을 추가하였고 이해하기 쉽게 예제를 일부 변경하였습니다. 문제가 되면 삭제하겠습니다.
비동기 프로그래밍 패러다임을 사용하면 IO 바운드 코드를 동시에 실행할 때 성능이 크게 향상될 수 있다(예: 채팅 모델 제공자에게 동시 API 요청을 보내는 경우).
그래프의 동기 구현을 비동기 구현으로 변환하려면 다음과 같은 작업이 필요하다.
- 노드에서
def대신async def를 사용하도록 업데이트한다. - 내부 코드를 적절히
await를 사용하여 업데이트한다.
LangChain의 많은 객체들이 Runnable 프로토콜을 구현하고 있으며, 이 프로토콜은 모든 동기 메서드에 비동기 버전이 존재하므로, 동기 그래프를 비동기 그래프로 업그레이드하는 것은 일반적으로 빠르게 할 수 있다.
준비
우선, 필요한 패키지를 설치하자.
pip install langgraph langchain_openai상태 준비
LangGraph에서 주요 그래프 유형은 StateGraph이다. 이 그래프는 각 노드에 전달되는 State 객체로 매개변수화된다. 각 노드는 그래프가 이 상태를 업데이트하는 데 사용하는 작업을 반환한다. 이 작업은 상태에서 특정 속성을 SET(예: 기존 값을 덮어씀)하거나 기존 속성에 ADD(추가)하는 방식으로 진행된다. SET 또는 ADD 여부는 그래프를 구성하는 데 사용하는 State 객체에 Annotated를 추가하여 표시한다.
이 예제에서는 추적할 상태가 단순히 메시지 목록이 될 것이다. 각 노드는 그 목록에 메시지를 추가하기만 하면 된다. 따라서 한 개의 키(messages)를 가진 TypedDict를 사용하고, 메시지 속성이 "추가 전용(append-only)"임을 Annotated로 표시할 것이다.
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]도구 준비
먼저 사용할 도구들을 정의한다. 도구를 만드는 것은 매우 쉽다. 이를 수행하는 방법에 대한 문서는 여기에서 확인할 수 있다.
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def search(query: str):
"""Call to surf the web."""
return ["질문에 대한 답변 내부에 있어"]
tools = [search]이제 도구들을 간단한 ToolNode로 래핑할 수 있다. 이는 도구 호출이 포함된 AIMessages를 메시지 목록으로 받아 도구들을 실행하고, 그 출력을 ToolMessages로 반환하는 간단한 클래스이다.
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)모델 준비
이제 사용하려는 챗 모델을 로드하자. 이 모델은 두 가지 조건을 만족해야 한다.
- 메시지와 함께 작동해야 한다. 상태는 주로 메시지 목록(채팅 기록)이기 때문이다.
- 도구 호출과 함께 작동해야 한다. 미리 구축된
ToolNode를 사용하고 있기 때문이다.
참고: 이러한 모델 요구 사항은 LangGraph 사용을 위한 필수 사항이 아니며, 이 특정 예제를 위한 요구 사항이다.
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")이후에 모델이 이러한 도구들을 호출할 수 있다는 것을 알려야 한다. 이를 위해 LangChain 도구를 함수 호출 형식으로 변환한 다음, 이를 모델 클래스에 바인딩할 수 있다.
model = model.bind_tools(tools)노드 정의
이제 그래프에서 여러 노드를 정의해야 한다. langgraph에서 노드는 함수나 실행 가능 객체일 수 있다. 이 예제에서는 두 가지 주요 노드가 필요하다.
- 에이전트: 무엇을 할지 (없다면 하지 않음) 결정하는 역할을 한다.
- 도구 호출을 실행하는 함수: 에이전트가 행동을 취하기로 결정하면, 이 노드는 그 행동을 실행한다.
또한 몇 가지 엣지를 정의해야 한다. 그 중 일부는 조건부 엣지가 될 수 있다. 조건부 엣지가 필요한 이유는 노드의 출력에 따라 여러 경로 중 하나가 선택될 수 있기 때문이다. 어느 경로를 선택할지는 해당 노드가 실행될 때까지 알 수 없다(LLM이 결정함).
- 조건부 엣지: 에이전트가 호출된 후, 다음과 같이 진행해야 한다: a. 에이전트가 행동을 취하라고 말하면, 도구 호출을 실행하는 함수가 호출되어야 한다. b. 에이전트가 작업을 마쳤다고 말하면, 종료되어야 한다.
- 정상 엣지: 도구가 호출된 후, 항상 에이전트로 돌아가서 무엇을 할지 결정해야 한다.
각 노드를 정의하고, 어떤 조건부 엣지를 선택할지 결정하는 함수를 정의해 보자.
수정 사항
각 노드를 async 함수로 정의한다.
from typing import Literal
def should_continue(state: State) -> Literal["end", "continue"]:
messages = state["messages"]
last_message = messages[-1]
if not last_message.tool_calls:
return "end"
else:
return "continue"
async def call_model(state: State):
messages = state["messages"]
response = await model.ainvoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}그래프 정의
이제 그래프를 정의할 수 있다.
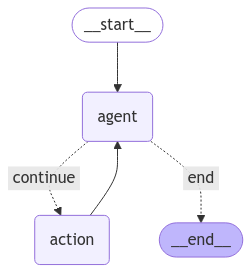
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph, START
workflow = StateGraph(State)
workflow.add_node("agent", call_model)
workflow.add_node("action", tool_node)
workflow.add_edge(START, "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
should_continue,
{
"continue": "action",
"end": END,
},
)
workflow.add_edge("action", "agent")
app = workflow.compile()display(
Image(
app.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png(
output_file_path="how-to-run-graph-asynchronously.png"
)
)
)
사용
다른 모든 LangChain 실행 가능한 객체들과 동일한 인터페이스를 제공한다.
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
inputs = {"messages": [HumanMessage(content="서울 날씨 어때?")]}
async def run():
result = await app.ainvoke(inputs)
print(result)
asyncio.run(run()){'messages': [HumanMessage(content='서울 날씨 어때?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='d1279cc5-0af0-4c77-a563-92c157bbdef2'), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_7vzE1MsLzw6iiRPiBN70f9Vs', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"서울 날씨"}', 'name': 'search'}, 'type': 'function'}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 15, 'prompt_tokens': 48, 'total_tokens': 63, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_0705bf87c0', 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-504f5177-38b7-4b45-a899-6910146e3ea5-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'search', 'args': {'query': '서울 날씨'}, 'id': 'call_7vzE1MsLzw6iiRPiBN70f9Vs', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 48, 'output_tokens': 15, 'total_tokens': 63, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}}), ToolMessage(content='["질문에 대한 답변 내부에 있어"]', name='search', id='df9f16f4-81b5-463c-8269-0cac60601c79', tool_call_id='call_7vzE1MsLzw6iiRPiBN70f9Vs'), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_lJueWPH3ULeSKaYRNHR1gXII', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"서울 날씨"}', 'name': 'search'}, 'type': 'function'}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 15, 'prompt_tokens': 81, 'total_tokens': 96, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_0705bf87c0', 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-d11d63de-d8d4-4d68-a017-7c860e7d7bcf-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'search', 'args': {'query': '서울 날씨'}, 'id': 'call_lJueWPH3ULeSKaYRNHR1gXII', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 81, 'output_tokens': 15, 'total_tokens': 96, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}}), ToolMessage(content='["질문에 대한 답변 내부에 있어"]', name='search', id='f6bceac0-0e0d-4217-9dba-afc1901d9260', tool_call_id='call_lJueWPH3ULeSKaYRNHR1gXII'), AIMessage(content='현재 서울의 날씨 정보는 제공할 수 없습니다. 하지만 서울의 날씨를 확인하고 싶으시다면 기상청 웹사이트나 날씨 앱을 이용해보시기 바랍니다.', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 42, 'prompt_tokens': 114, 'total_tokens': 156, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_0705bf87c0', 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-07aac903-df0d-49ae-9367-6fac7d121fcb-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 114, 'output_tokens': 42, 'total_tokens': 156, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}})]}조금 시간이 걸릴 수 있다. 백그라운드에서 몇 가지 호출을 처리하고 있기 때문이다. 진행 중인 결과를 실시간으로 확인하려면 스트리밍을 사용할 수 있다. 이에 대한 자세한 정보는 아래를 참조하자.
Streaming
LangGraph는 여러 가지 유형의 스트리밍을 지원한다.
노드 출력을 스트리밍하기
LangGraph를 사용하면 각 노드에서 생성되는 출력을 쉽게 스트리밍할 수 있다는 이점이 있다.
inputs = {"messages": [HumanMessage(content="서울 날씨 어때?")]}
async def run():
async for output in app.astream(inputs, stream_mode="updates"):
# stream_mode="updates"는 노드 이름으로 키가 지정된 dict 출력을 생성한다.
for key, value in output.items():
print(f"Output from node '{key}':")
print("---")
print(value["messages"][-1].pretty_print())
print("\n---\n")Output from node 'agent':
---
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
search (call_MGPexdTsTCKFROKQeKmxOAj9)
Call ID: call_MGPexdTsTCKFROKQeKmxOAj9
Args:
query: 서울 날씨
None
---
Output from node 'action':
---
================================= Tool Message =================================
Name: search
["질문에 대한 답변 내부에 있어"]
None
---
Output from node 'agent':
---
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Tool Calls:
search (call_COLzuZmZpjAZNG5ru5383JZc)
Call ID: call_COLzuZmZpjAZNG5ru5383JZc
Args:
query: 서울 현재 날씨
None
---LLM 토큰을 스트리밍하기
각 노드에서 생성되는 LLM 토큰에 접근할 수도 있다. 이 경우 "agent" 노드만 LLM 토큰을 생성한다. 제대로 작동시키려면 스트리밍을 지원하는 LLM을 사용하고, LLM을 생성할 때 스트리밍을 설정해야 한다 (예: ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-1106", streaming=True)).
async def run():
inputs = {"messages": [HumanMessage(content="what is the weather in sf")]}
async for output in app.astream_log(inputs, include_types=["llm"]):
# astream_log()은 요청된 로그 (여기서는 LLM)를 JSONPatch 형식으로 생성한다.
for op in output.ops:
if op["path"] == "/streamed_output/-":
# this is the output from .stream()
...
elif op["path"].startswith("/logs/") and op["path"].endswith(
"/streamed_output/-"
):
try:
content = op["value"].content[0]
if "partial_json" in content:
print(content["partial_json"], end="|")
elif "text" in content:
print(content["text"], end="|")
else:
print(content, end="|")
except:
pass
asyncio.run(run()){'id': 'toolu_01ULvL7VnwHg8DHTvdGCpuAM', 'input': {}, 'name': 'search', 'type': 'tool_use', 'index': 0}||{"|query": "wea|ther in |sf"}|
Base|d on the search results|, it looks| like the current| weather in San Francisco| is:
-| Partly| clou|dy with a high| of 65|°F (18|°C) an|d a low of |53|°F (12|°C). |
- There| is a 20|% chance of rain| throughout| the day.|
-| Winds are light at| aroun|d 10| mph (16| km/h|).
The| weather in San Francisco| today| seems| to be pleasant| with| a| mix| of sun and clouds|. The| temperatures| are mil|d, making| it a nice| day to be out|doors in| the city.|LangGraph 참고 자료
- Controllability
- Persistence
- Memory
- Human-in-the-loop
- Streaming
- Tool calling
- Subgraphs
- State Management
- Other
- Prebuilt ReAct Agent

