complete guide to elasticsearch를 정리한 자료입니다.
https://www.udemy.com/course/elasticsearch-complete-guide/
37. analysis 소개
Analysis
- text analysis라고 불린다.
- text 필드/값에 적용된다.
- text 값은 문서를 인덱싱할 때 분석된다.
- 결과는 효과적인 검색을 위해 데이터 구조에 저장된다.
- _source 객체는 문서 검색할 때는 사용되지 않는다.
- 문서 인덱싱할 때 정확한 값을 포함한다.
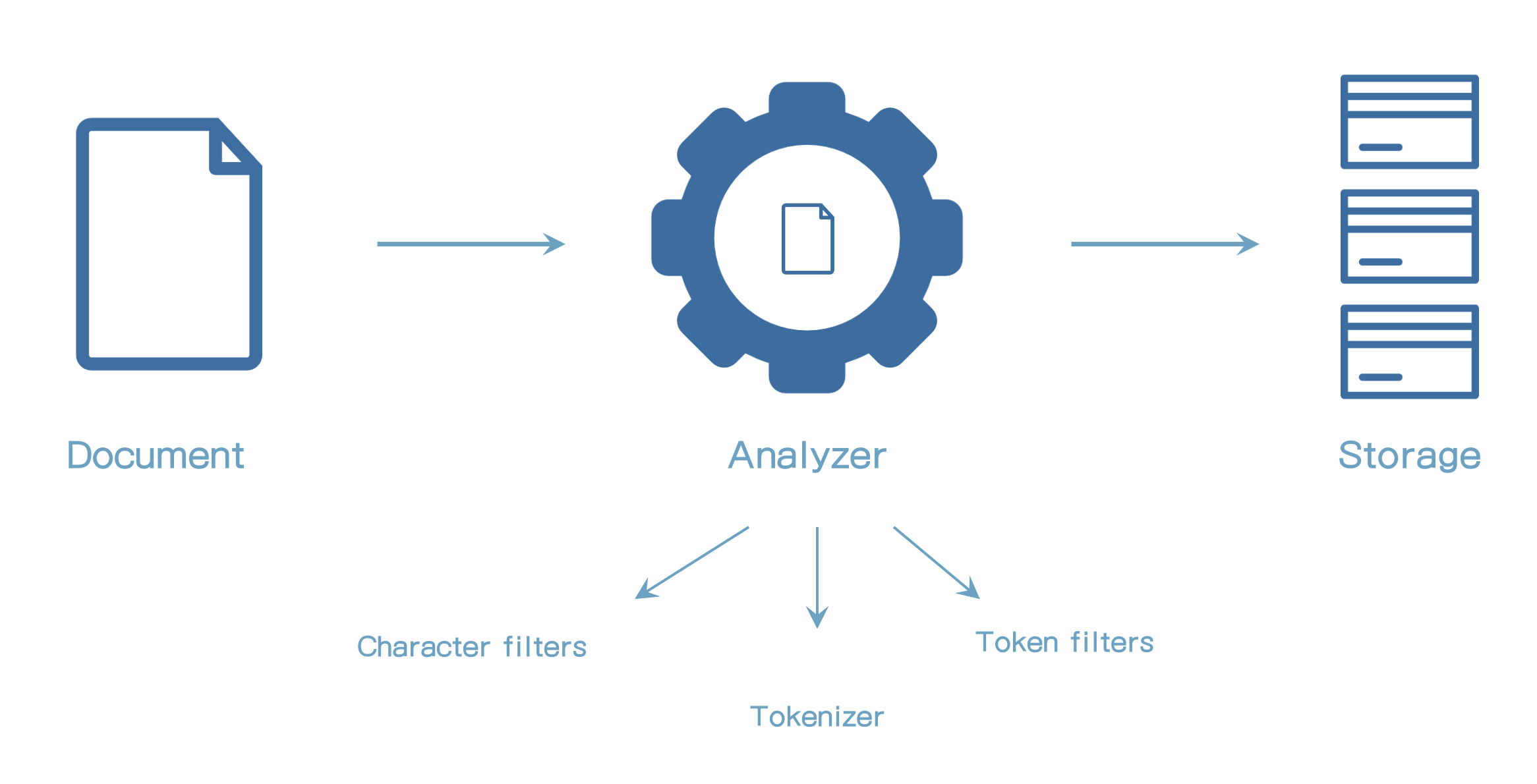
- analyzer는 3가지 블록으로 구성되어 있다. (character filters, tokenizer, token filters)
- text를 analyzing하는 결과는 검색가능한 데이터 구조에 저장된다.
Character filters
- 원본 문자를 받아서 추가, 삭제, 변경을 통해 변형된다.
- Analyzer는
0개 이상의 character filter를 포함한다. - character filter는 정의된 순서대로 적용된다.
- 예(html_stripe 필터)
- Input: "I'm in a good mood - and I love açaí!"
- Output: "I'm in a good mood - and I love açaí!"
Tokenizers
- Analyzer는
하나의tokenizer를 포함한다. - 문자를 토크나이징한다. 예) 토큰으로 짜른다.
- 문자는 토큰의 부분으로 자른다.
- 예
- Input: "I REALLY like beer!"
- Output: ["I", "REALLY", "like", "beer"]
Token filters
- 입력으로 토크나이저이ㅡ 결과를 받는다. (Ex: 토큰)
- token filter는 토큰을 추가, 수정, 삭제할 수 있다.
- analyzer는
0개 이상의 token filter를 가진다. - token filter는 정의된 순서대로 적용된다.
- 예: lowercase filter
- Input: ["I", "REALLY", "like", "beer"]
- Output: ["i", "really", "like", "beer"]
built-in, custom 컨포넌트
- Built-in analyzer, character filters, token filters를 사용할 수 있다.
- 또한 Custom analyzer를 사용할 수 있다.
[default analyzer의 동작방식]
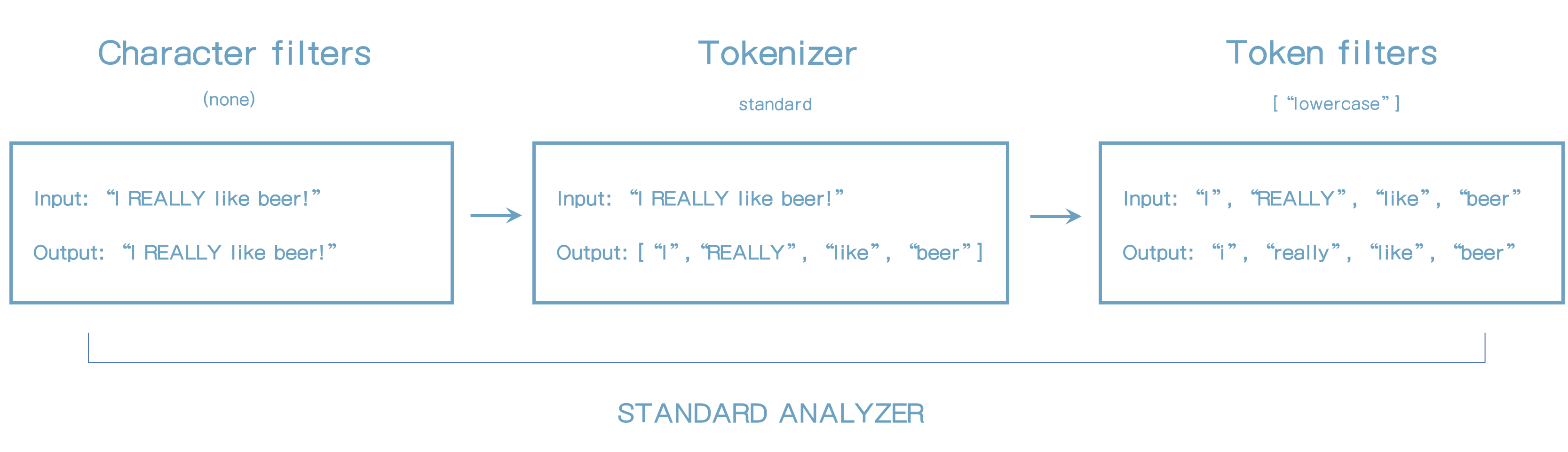
38. Analyzer API 사용하기
아래 문장을 analyzer로 실행하면 standard analyzer로 실행이 된다.
POST _analyze
{
"text": "2 guys walk into a bar, but the third... DUCKS! :-)",
"analyzer": "standard"
}Standard analyzer는 특수문자는 모두 제거한다.
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "2",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<NUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "guys",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "walk",
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "into",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 16,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "a",
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 20,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "bar",
"start_offset" : 21,
"end_offset" : 24,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "but",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 29,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "the",
"start_offset" : 30,
"end_offset" : 33,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "third",
"start_offset" : 34,
"end_offset" : 39,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "ducks",
"start_offset" : 43,
"end_offset" : 48,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 9
}
]
}이는 아래와 같다.
POST _analyze
{
"text": "2 guys walk into a bar, but the third... DUCKS! :-)",
"char_filter": [],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
}39. 역색인(inverted indices) 이해하기
소개
- 필드값들이 여라가지 데이터 구조 중 하나로 저장된다.
- 데이터 구조는 필드 데이터 유형에 따라 다르다.
- 효율적인 데이타 접근을 보장한다 - 예. 검색
- Elasticsearch가 아니라 아파치 루씬이 처리한다.
- 이번 내용은 역색인에 초점을 두고 있다.
역색인
- 텀(term) 사이 매핑과 어느 문서가 포함하는가
- 분석기 외부 관점에서는 텀(term)이라는 용어를 사용한다.
- 토큰(token)이라는 용어는 분석기 관점에서만 사용된다.
- 대부분은 텀(term)이라고 사용한다.
- 텀(term)은 알파벳순으로 정렬되어 있다.
- 역색인은 단순히 텀(term)과 문서 ID보다 더 많은 정보를 가지고 있다.
- 예) 스코어를 위한 정보
- 하나의 텍스트 필드 당 하나의 역색인 파일이 생긴다.
- 예를 들면 다른 데이터 타입은 BKD 트리를 사용한다. (예: 숫자, 날짜, 위치)
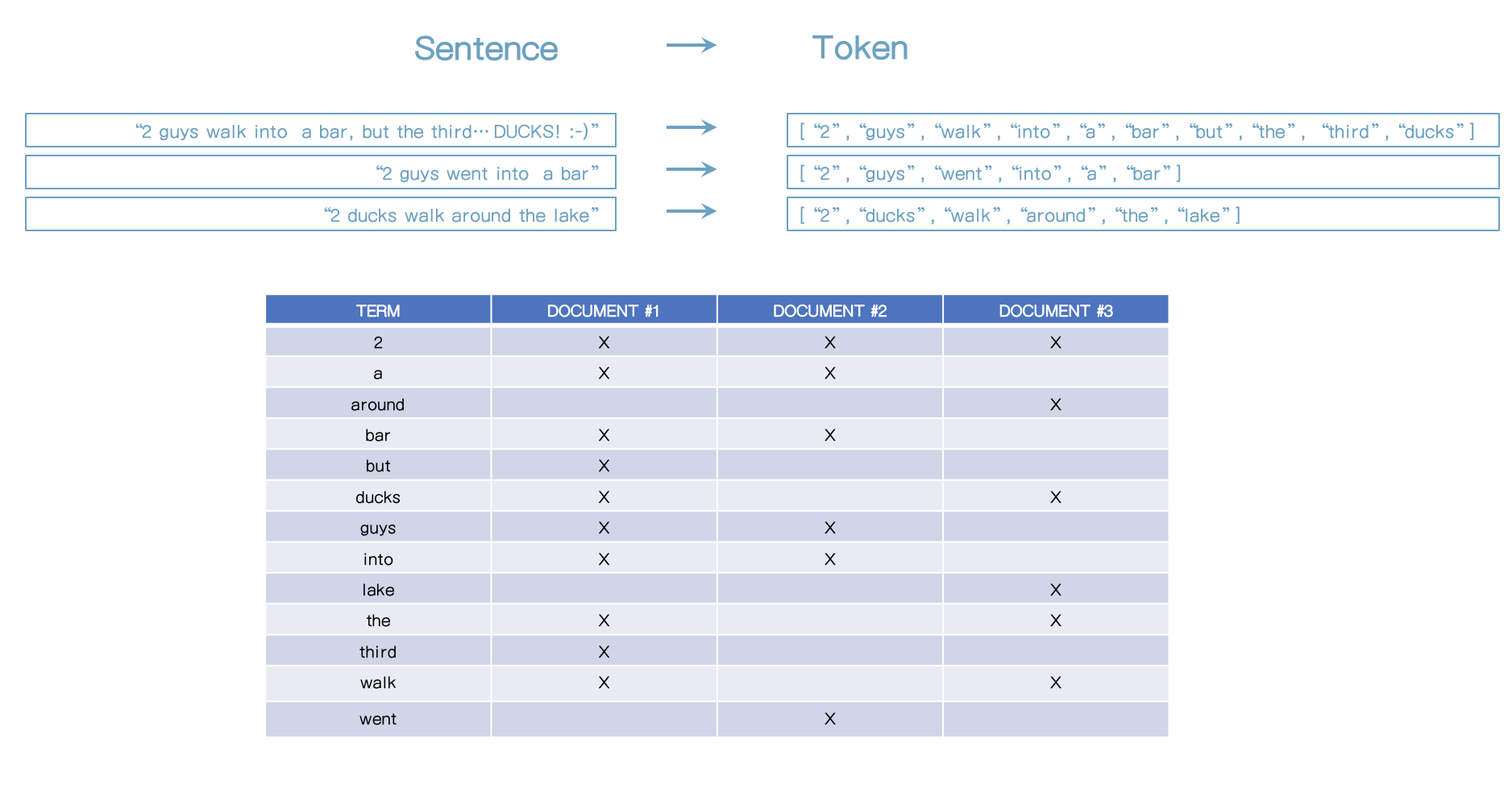
- ducks 를 검색할 때 역색인에서 어느 문서가 ducks를 포함하고 있는지 확인하면 된다. (#1, #3)
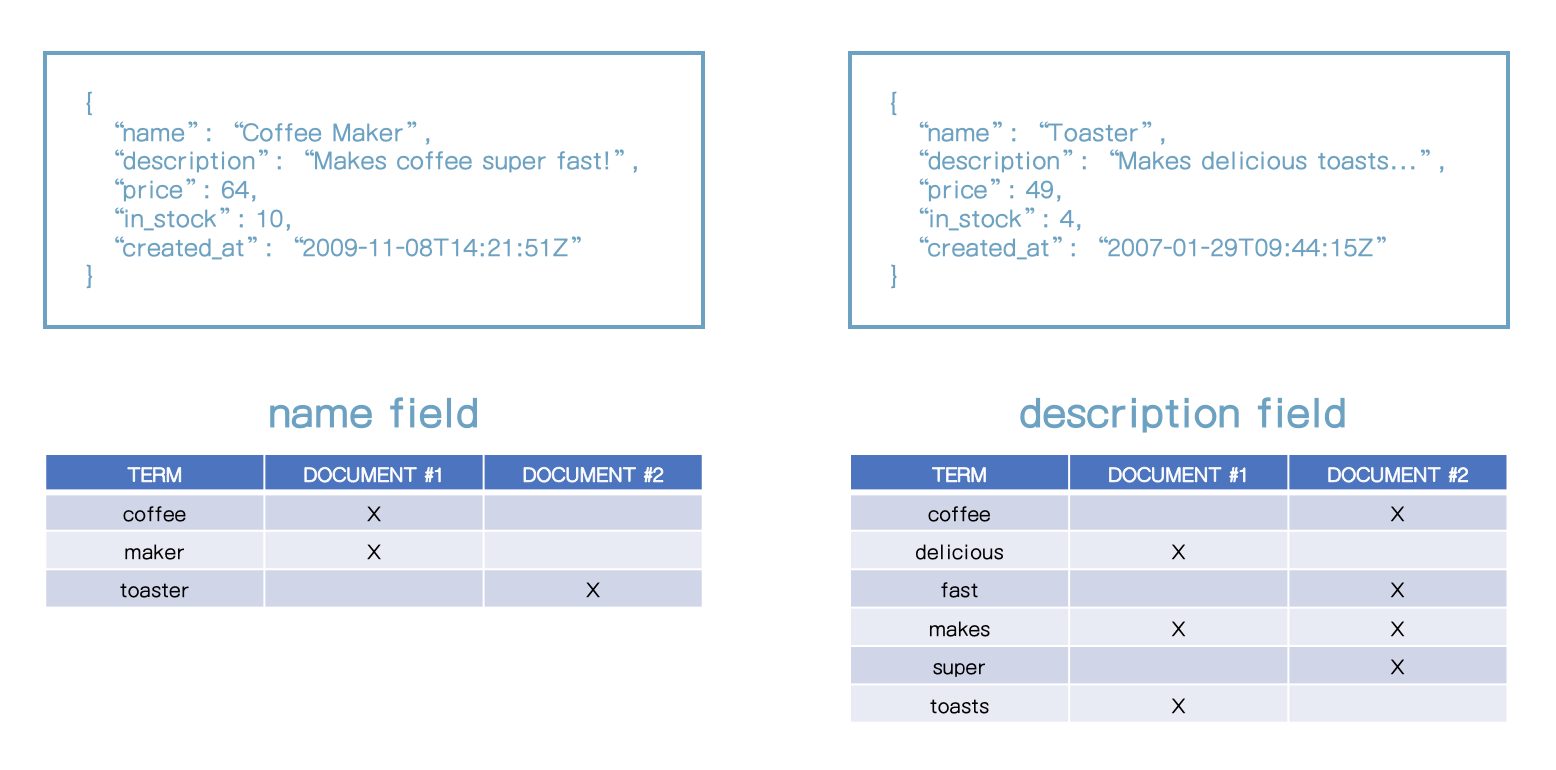
- 위와 같이 다른 2개의 문서를 인덱싱을 하면 역색인 파일은 각 필드별로 각각 만들어진다. (name 필드, description 필드)
40. Mapping 소개
mapping은 무엇인가?
- 문서 구조를 정의한다 (예: 필드와 데이터 타입)
- 또한 값이 어떻게 인덱싱되는지 구성하는데 사용
- 관계형 DB에서 테이블 스키마와 유사
- 명시적인(Explicit) 매핑
- 우리가 직접 필드 매핑을 정의
- 동적(Dynamic) 매핑
- elasticsearch가 필드 매핑을 정의한다.
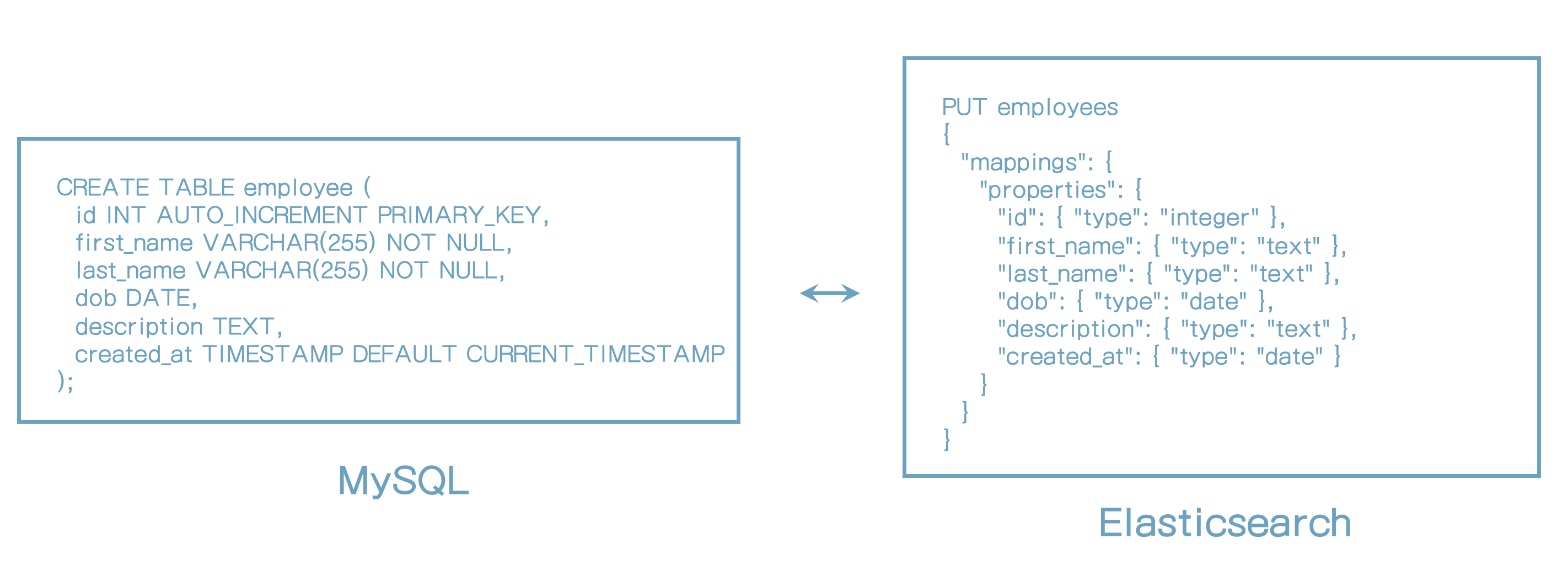
41. 데이터 타입
object, text, float, boolean, interger, double, short, date
object 데이터 타입
- JSON object에 사용
- objects는 nested가 될 수 있다.
- Properties 파라미터를 사용하여 매핑된다.
- objects는 루씬(Lucene)에 객체로 저장되지 않는다.
- objects는 유효한 JSON을 인덱싱할 수 있도록 변형된다.
- 특별한 경우에 objects는 flatten된다.
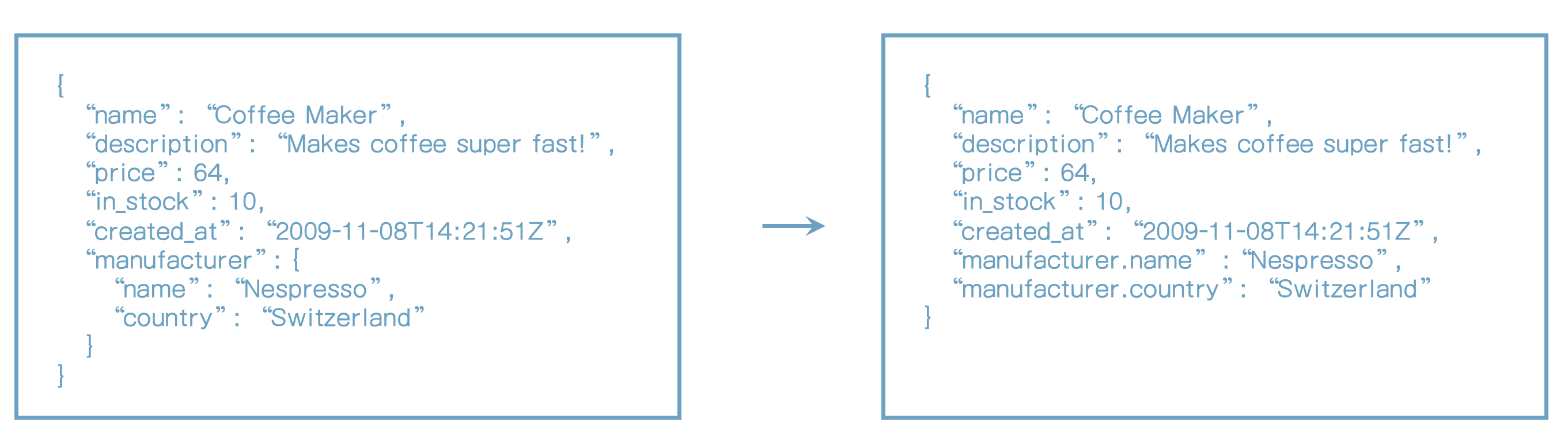
객체 array인 경우는 아래처럼 저장된다.
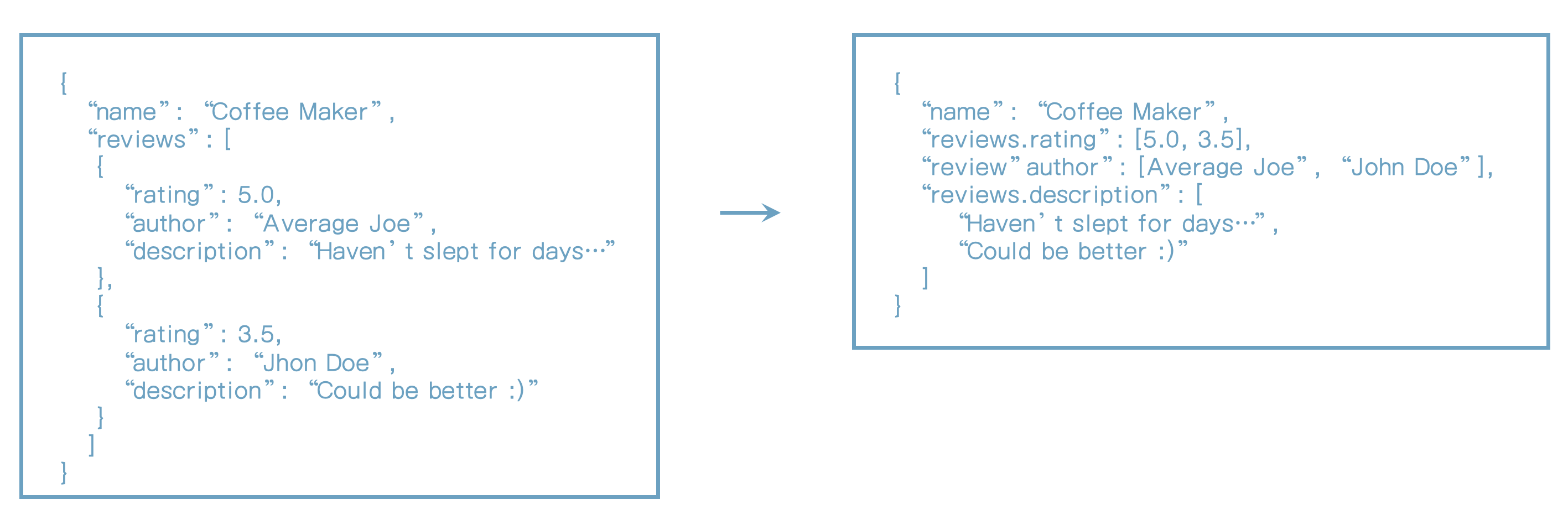
QUERY: MATCH products WHERE review.author == "John Doe" AND reviews.rating >= 4.0위와 같이 쿼리를 실행하면 해당 문서가 검색되는 것으로 나온다. 하지만 실제로는 John Doe는 3.5이라서 검색되지 않아야 한다.
이는 우리가 원하는 결과가 아니다.
nested 데이터 타입
- Object 데이터 타입과 유사하지만 객체간의 관계를 유지한다.
- objects 배열을 인덱싱할 때 유용하다.
- 독립적으로 objects를 쿼리할 수 있게 한다.
- nested 쿼리를 사용해야 한다.
- nested object는 숨겨진 문서로 저장된다.
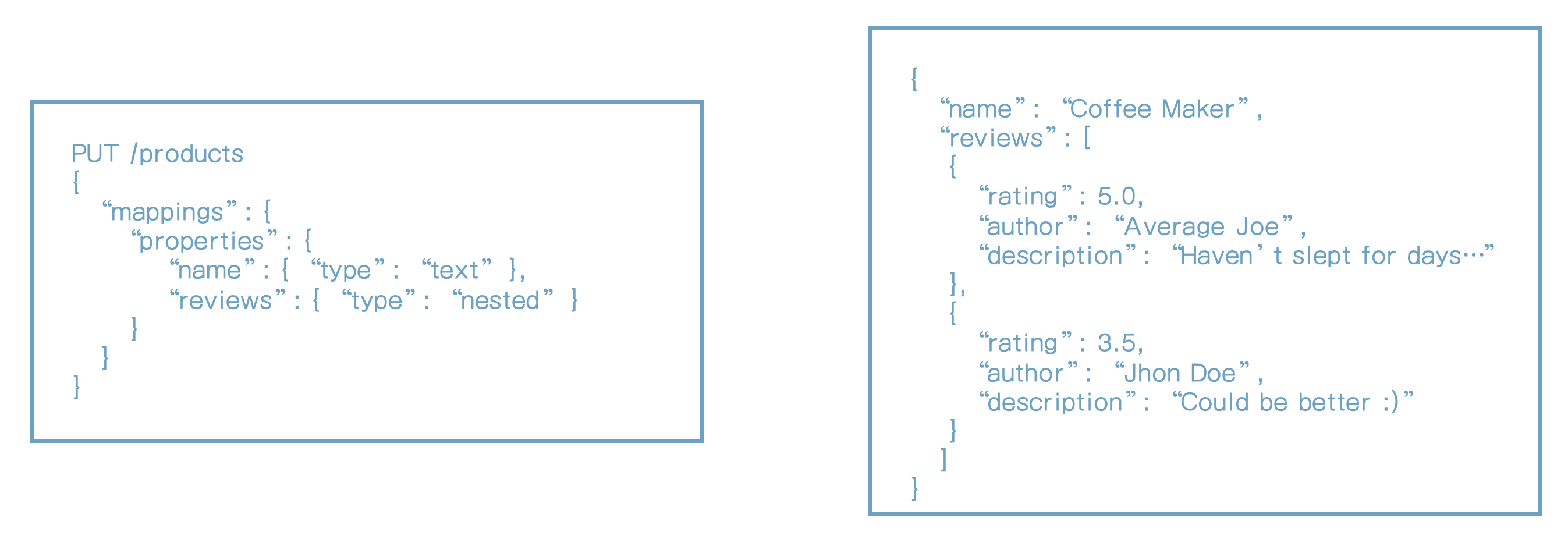
QUERY: MATCH products WHERE review.author == "John Doe" AND reviews.rating >= 4.0객체는 독립적으로 저장되기 때문에 쿼리는 예상대로 동작한다.
루씬은 object의 개념이 없기 때문에 이러한 객체는 어떻게 저장될까?
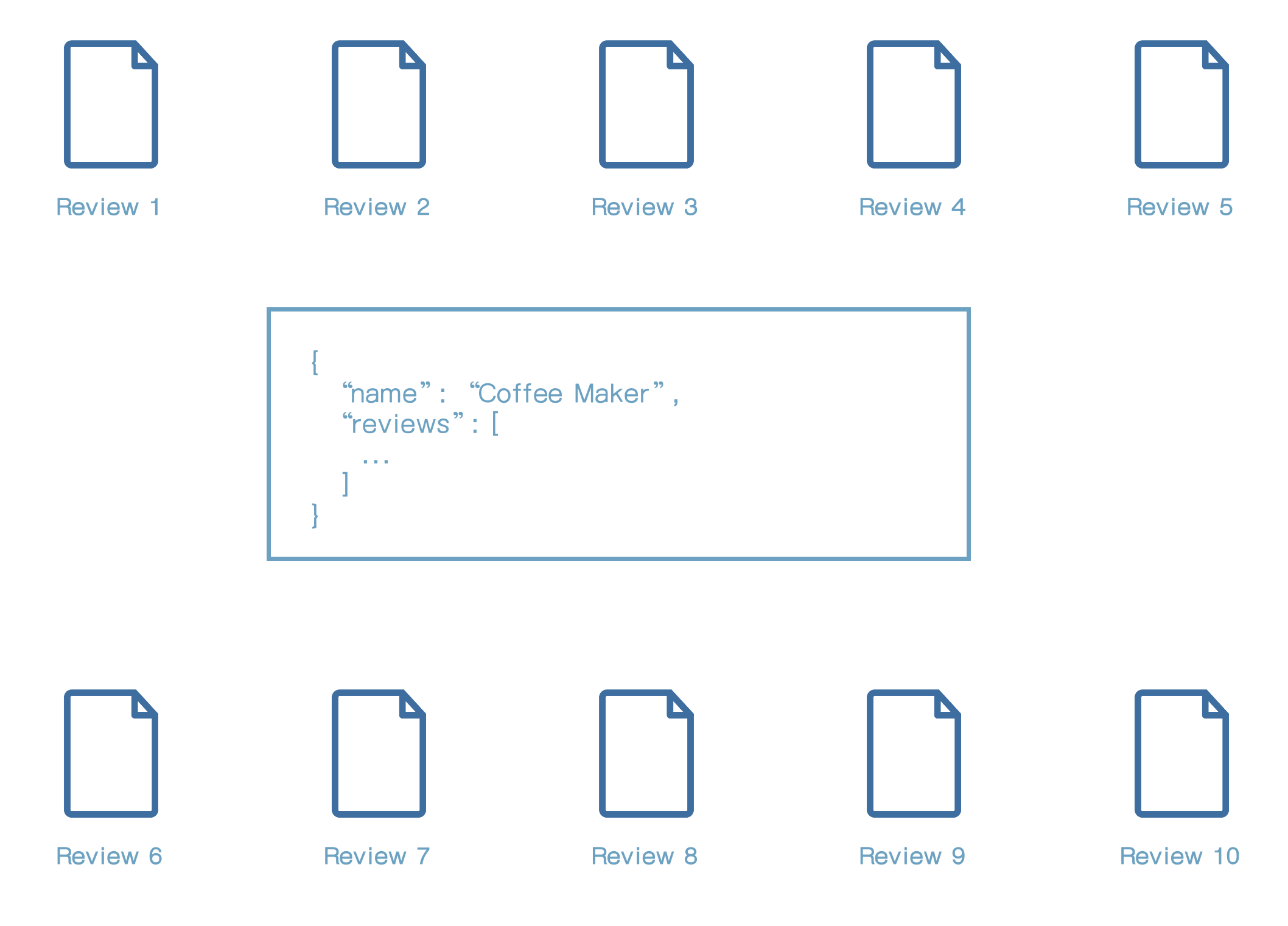
위와 같이 review를 10개 가진 하나의 문서(product)를 저장하면 총 11개의 문서가 저장된다. (1개의 product + 10개의 review)
keyword 데이터 타입
- 정확한 값이 일치할 때 사용
- 일반적으로 필터링, 집합(aggregation), 정렬에 사용된다.
- 예) PUBLISHED 상태의 기사를 검색
- Full-text 검색을 위해서는 text 데이터 타입을 사용해라.
- 예) 기사 내용을 검색
42. Keyword 데이터 유형은 어떻게 동작하는가?
keyword 필드는 어떻게 분석되는가?
- Keyword 필드는 keyword analyzer로 분석된다.
- keyword analyzer는 no-op analyzer이다. (어떤 것도 하지 않는다는 뜻)
- 단일 토큰으로 수정되지 않은 문자열을 출력
- 이 토큰이 역색인 파일에 추가된다.
- keyword 필드는 정확히 일치, 집합(aggregation), 정렬에 사용된다.
POST _analyze
{
"text": "2 guys walk into a bar, but the third... DUCKS! :-)",
"analyzer": "keyword"
}{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "2 guys walk into a bar, but the third... DUCKS! :-)",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 53,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}43. type coercion 이해
- 데이터 유형이 문서 인덱싱될 때 확인된다.
- 검증되고 유효하지 않은 값들은 실패한다.
- 예) text 필드에 객체 인덱싱할 때
- 때로는, 잘못된 데이터 타입도 가능하다.
아래 쿼리를 차례대로 실행하자.
PUT coercion_test/_doc/1
{
"price": 7.4
}price에 float 타입으로 자동으로 지정된다.
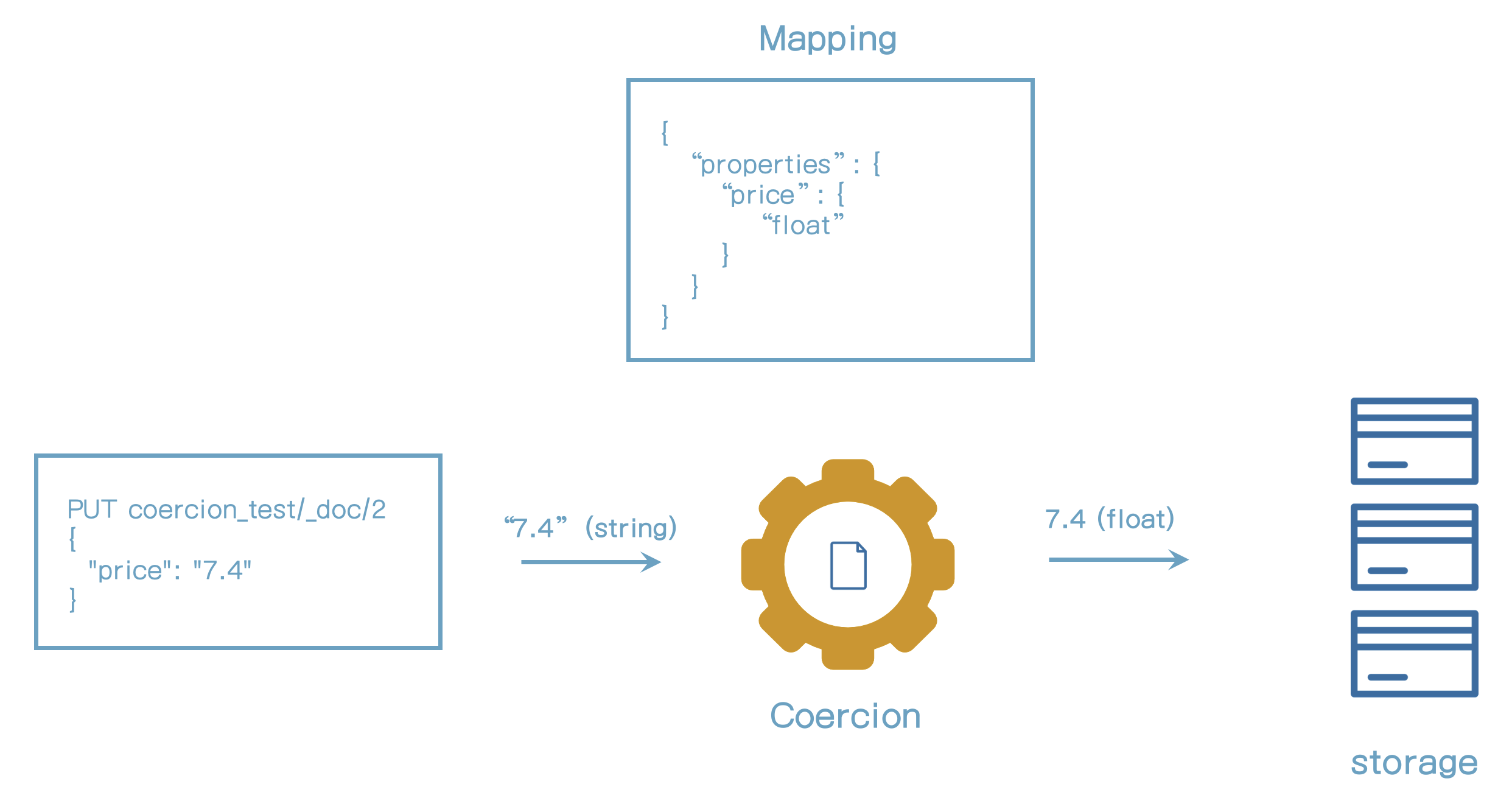
PUT coercion_test/_doc/2
{
"price": "7.4"
}"7.4" 문자열 입력 시 7.4의 float타입으로 변경되어 저장된다.
PUT coercion_test/_doc/3
{
"price": "7.4m"
}"7.4m" 문자열 입력 시 float 타입으로 변경을 할 수 없으므로 실패한다.
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [price] of type [float] in document with id '3'. Preview of field's value: '7.4m'"
}
],
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [price] of type [float] in document with id '3'. Preview of field's value: '7.4m'",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "number_format_exception",
"reason" : "For input string: \"7.4m\""
}
},
"status" : 400
}조회를 해보자.
GET coercion_test/_doc/1{
"_source" : {
"price" : 7.4
}
}7.4 float타입으로 조회된다.
2번 문서를 조회하면
GET coercion_test/_doc/2{
"_source" : {
"price" : "7.4"
}
}"7.4" 문자열로 저장된다.
_source object 이해
- 인덱싱할 때 주어진 값을 가진다. ("7.4")
- 인덱싱된 값이 아니다 (7.4)
- 검색 쿼리는 인덱싱된 값을 사용한다. (_source값이 아니다)
- BKD tree, 역색인, etc
- _source는 값이 어떻게 인덱싱되었는지를 나타내지 않는다.
- _source에서 값을 사용하려면 coercion를 명심해라.
- 이 예제에서는 string 혹은 float이 될 수 있다.
몇 가지 더
- Integer 필드에 floating point를 넣으면 integer로 들어갈 것이다.
- coercion은 동적 매핑에서는 사용되지 않는다.
- 새 필드에 "7.4"를 넣으면 text 매핑을 만들것이다.
- 항상 올바른 데이터 유형을 사용하도록 노력해라.
- 특히 필드를 처음 인덱싱 할 때
- coercion을 비활성화 하는 것은 선택사항이다.
- 기본값은 enabled이다.
44. Arrays 이해
- Array 데이터 타입 같은 것은 없다.
- 어떤 필드도 0개 이상의 값을 가질수 있다.
- 특별한 설정이나 매핑정보가 필요 없다.
- 문서 인덱싱할 때 array를 사용하면 된다.
- Product 인덱스에 tags 필드를 사용했었다.
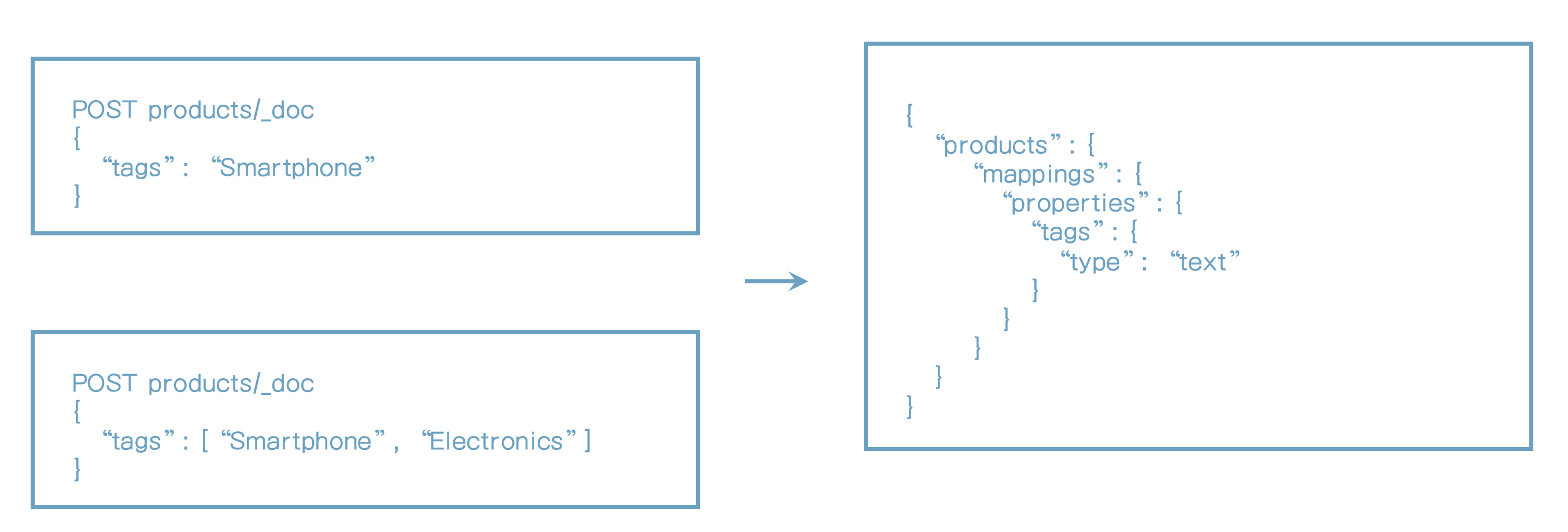
array를 위한 특별한 표시는 없다.
내부적으로 어떻게 저장이 되는 걸까?
{
"text": ["Strings are simply", "merged together"],
"analyzer": "standard"
}{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "strings",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "are",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "simply",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 18,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "merged",
"start_offset" : 19,
"end_offset" : 25,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "together",
"start_offset" : 26,
"end_offset" : 34,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
}
]
}이 의미는 string은 배열이 아니라 하나의 문자열로 취급된다는 의미이다.
제약사항
- Array 값은 동일한 데이터 타입이어야 한다.
// correct data type
[ "electronics", "expensive", "popular" ]
[ 37, 45, 9 ]
[ true, false, true ]
[ {"name": "Coffee Maker"}, {"name": "Toaster"}, {"name": "Blendar"} ]
//coercion
[ true, false, "true"]
[ "electronics", "expensive", 47]
[ 37, 45, "9" ]
[ true, false, "true" ]
// cannot coercion
[ {"name": "Coffee Maker"}, {"name": "Toaster"}, false]- Coercion은 이미 매핑된 필드에서만 동작한다.
- 동적 매핑으로 필드 매핑을 만들려면 array는 동일한 데이터 타입이어야 한다.
- coercion을 추천하지 않는다. (적어도 의도적으로는 사용하지 마라)
Nested arrays
- Arrays는 nested array를 포함할 수도 있다.
- Arrays는 인덱싱될 때 flatten 된다.
- [ 1, [2, 3] ]은 [ 1, 2, 3 ]이 된다.
array 객체를 독립적으로 조회하려면 nested 데이터 타입을 사용해야 한다는 것을 꼭 기억하자.
45. 명시적인 매핑 추가
PUT reviews
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"rating": { "type": "float" },
"content": { "type": "text" },
"product_id": { "type": "integer" },
"author": {
"properties": {
"first_name": { "type": "text" },
"last_name": { "type": "text" },
"email": { "type": "keyword" }
}
}
}
}
}PUT reviews/_doc/1
{
"rating": 5.0,
"content": "Outstanding course! Bo really taught me a lot about Elasticsearch!",
"product_id": 123,
"author": {
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"email": {}
}
}성공적으로 인덱싱된다.
email필드에 객체를 저장해보자.
PUT reviews/_doc/1
{
"rating": 5.0,
"content": "Outstanding course! Bo really taught me a lot about Elasticsearch!",
"product_id": 123,
"author": {
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"email": {}
}
}인덱싱이 실패하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [author.email] of type [keyword] in document with id '1'. Preview of field's value: '{}'"
}
],
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [author.email] of type [keyword] in document with id '1'. Preview of field's value: '{}'",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "illegal_state_exception",
"reason" : "Can't get text on a START_OBJECT at 8:14"
}
},
"status" : 400
}46. 매핑 조회
GET reviews/_mapping결과는 아래와 같다.
{
"reviews" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"author" : {
"properties" : {
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"first_name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"last_name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
"content" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"product_id" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"rating" : {
"type" : "float"
}
}
}
}
}특정 필드(content)를 조회
GET reviews/_mapping/field/content결과는 아래와 같다.
{
"reviews" : {
"mappings" : {
"content" : {
"full_name" : "content",
"mapping" : {
"content" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}
}author.email 필드를 조회
GET reviews/_mapping/field/author.email결과는 아래와 같다.
{
"reviews" : {
"mappings" : {
"author.email" : {
"full_name" : "author.email",
"mapping" : {
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}47. 필드명에 .(dot)을 사용하기
PUT reviews_dot_notation
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"rating": { "type": "float" },
"content": { "type": "text" },
"product_id": { "type": "integer" },
"author.first_name": { "type": "text" },
"author.last_name": { "type": "text" },
"author.email": { "type": "keyword" }
}
}
}mapping을 조회하자.
GET reviews_dot_notation/_mapping결과는 아래와 같다.
elasticsearch는 결과를 아래와 같이 json 형식으로 변형을 한다.
{
"reviews_dot_notation" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"author" : {
"properties" : {
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"first_name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"last_name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
"content" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"product_id" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"rating" : {
"type" : "float"
}
}
}
}
}객체로 설정한 것과 결과가 같다.
48. 기존 인덱스에 매핑 추가하기
Review 인덱스에 created_at 추가하기
PUT reviews/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"created_at": { "type": "date" }
}
}49. elasticsearch에 date는 어떻게 동작하는가?
date 필드 소개
- 3가지 중 하나의 방법으로 정의된다.
- Formatted 문자
- Epoch(long) 이후 milliseconds
- Epoch(integer) 이후 seconds
- epoch는 1970년 1월 1일을 말한다.
- Custom format이 지원된다.
date 필드의 기본 동작
- 3가지 지원 포맷
- time이 없는 date
- time이 있는 date
- epoch(long) 이후 milliseconds
- 어떤 것도 설정되지 않으면 UTC timezone이라고 판단
- Date는 ISO 8701 명세에 의해 포맷팅되어야 한다.
date 필드는 어떻게 저장되는가
- 내부적으로 epoch(long) 이후 milliseconds로 저장된다.
- 인덱싱 때 제공한 값은 내부적으로 long 으로 변형된다.
- Date는 UTC timestamp로 변형된다.
- 조회할 때도 동일하게 변형된다.
50. 필드를 생략하면 어떻게 처리될까?
필드 생략
- 모든 필드는 선택사항이다.
- 문서를 인덱싱할 때 필드를 생략할 수 있다.
- 예) null값을 허용하는 RDB와는 다르다.
- 애플리케이션 레벨에서 무결성 체크가 필요하다.
- 예) 필수값
- 필드매핑을 추가하는 것은 필드를 필수값으로 만들지는 않는다.
- 검색은 자동으로 생략된 필드를 처리한다.
51. 매핑 파라미터
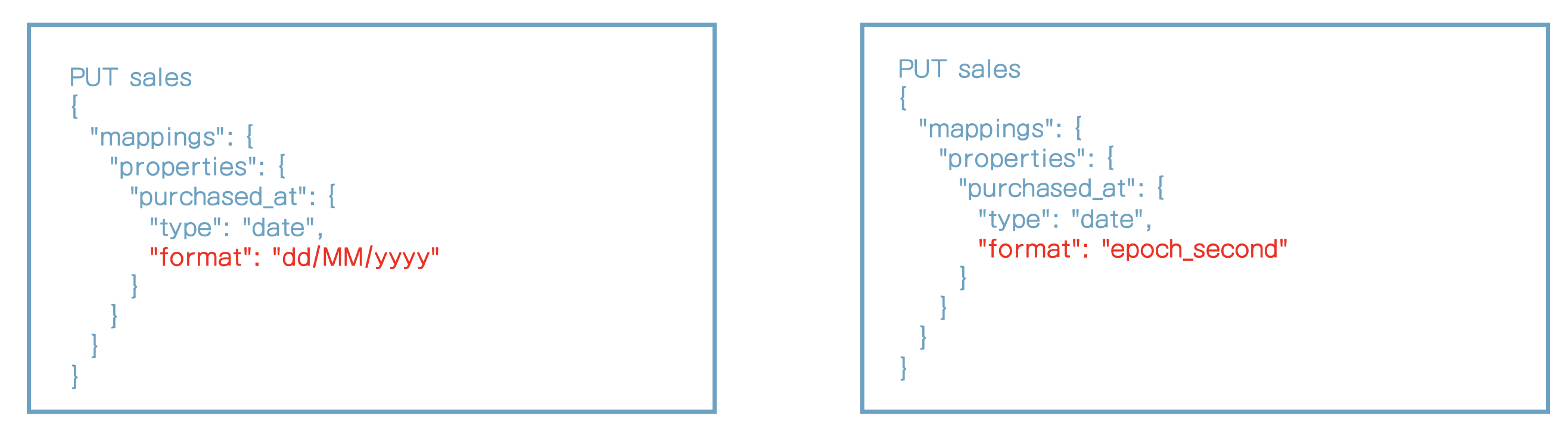
format 파라미터
- Date 필드의 포맷을 정의
- 가능하다면 기본 포맷을 사용하기를 권장
- "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis"
- java의 DateFormatter 구문 사용하기
- 예) "dd/MM/yyyy"
- 내장 포맷 사용하기
- 예) "epoch_second"
properties 파라미터
- object와 nested 필드의 nested 필드를 정의한다.

coerce 파라미터
- 값의 coercion을 가능/불가능하게 한다. (기본값: enabled)

doc_values 소개
- elasticsearch는 다양한 데이터 구조를 사용한다.
- 하나의 데이터 구조는 다양한 용도로 사용하지 못한다.
- 역색인은 text를 검색하는데 효과적이다.
- 이 타입은 다른 다양한 패턴을 잘 처리하지 못한다.
- "Doc values"는 루씬에서 사용되는 다른 데이터 구조이다.
- 다른 데이터 패턴에 최적화되어 있다 (document -> terms)
- 특히 inverted되지 않은 역색인
- 정렬, 집합, 스크립팅
- 대체용이 아닌 추가적인 데이터 구조이다.
- elsticsearch는 자동으로 적절한 데이터 구조를 조회한다.
doc_values 비활성화
- 디스크 저장공간을 절약하기 위해 doc_values를 false로 설정
- 인덱싱 속도를 약간 증가시킨다.
- 집합, 정렬, 스크립팅을 사용하지 않는다면 doc values를 비활성화해라.
- 특히 대규모 인덱스에 유용하다. 작을 때는 의미 없다.
- 문서를 새 인덱스로 reindexing하지 않고는 변경될 수 없다.
norms 파라미터
- scoring을 위한 Normalization 요소
- 종종 결과를 필터링하지 않고 순위를 매길수 있다.
- Norms는 디스크 공간을 저장하기 위해 비활성화 될 수 있다.
- scoring에 사용되지 않는 필드에 유용하다.
- 여전히 필드는 필터링과 집합에 사용될 수 있다.
index 파라미터
- 필드를 인덱싱하지 않는다.
- 값은 여전히 _source 내에 저장된다.
- 필드를 검색쿼리에서 사용하지 않을 때 유용하게 사용될 수 있다.
- 디스크 공간 절약하는 것은 인덱싱 속도를 약간 증가시킨다.
- 종종 time series 데이터에 사용된다.
- indexing을 disabled한 필드는 여전히 집합(aggregation)에 사용될 수 있다.
null_value 파라미터
- NULL 값은 인덱싱 혹은 검색될 수 없다.
- NULL값을 다른 값으로 변경하기 위해 이 파라미터를 사용해라.
- NULL 값에서만 동작한다.
- 변경될 값은 필드의 데이터 타입과 동일해야 한다.
- _source내에 저장된 값에는 영향을 주지 않는다.
copy_to 파라미터
- 다양한 필드 값을 group 필드로 복사하는 데 사용
- 단순히 대상 필드의 이름을 값으로 명시
- 예) first_name과 last_name -> full_name
- term/token이 아닌 값이 복사된다.
- 대상 필드의 analyzer는 값에 대해 사용된다.
- 대상 필드는 _source의 일부분이 아니다.
52. 기존 매핑 수정
- product ID는 문자를 포함한다고 하자.
- product_id 필드의 데이터 타입을 text 혹은 keyword로 변경하자
- Full-text 검색으로 사용하지 않을 것이다.
- 필터링 용으로 사용해서 keyword 데이터 타입이 좋다.
기존에 integer로 되어 있는 product_id를 keyword로 변경하자.
PUT reviews/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"product_id": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "mapper [product_id] of different type, current_type [integer], merged_type [keyword]"
}
],
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "mapper [product_id] of different type, current_type [integer], merged_type [keyword]"
},
"status" : 400
}오류가 발생한다.
매핑 수정의 제약사항
- 일반적으로 elasticsearch 필드 매핑은 변경될 수 없다.
- 새 필드 매핑을 추가할 수 있다.
- 몇 개의 매핑 파라미터는 기존 매핑에 수정될 수 있다.
email필드에 ignore_above를 추가
PUT reviews/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"author": {
"properties": {
"email": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}- 매핑을 수정하는 것은 기존 문서에 문제가 될 수 있다.
- 예를 들면 Text 값은 이미 분석되었다.
- 어떤 데이터 타입간의 변경이 전체 데이터 구조를 새로 만들어야 할 수도 있다.
- 인덱스에 데이터가 없는 경우라도 매핑을 수정할 수 없다.
- 필드 매핑은 삭제될 수 없다.
- 다만 문서를 인덱싱할 때 필드를 남겨둔다.
- update by query API는 디스크 공간을 복구하는데 사용될 수 있다.
- 해결책은 문서를 새 인덱스로 reindex하는 것이다.
53. Reindex API로 문서를 재색인하기
PUT reviews_new
{
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"author" : {
"properties" : {
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
},
"first_name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"last_name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
"content" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"created_at" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"product_id" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"rating" : {
"type" : "float"
}
}
}
}
}reviews를 reviews_new로 reindex해보자.
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "reviews"
},
"dest": {
"index": "reviews_new"
}
}_source 데이터 타입
- 데이터 타입은 값이 어떻게 인덱싱되는지 반영되지 않는다.
- _source 는 인덱싱될 때 제공된 필드값을 포함한다.
- 검색 결과에 _source값을 사용하는 것이 일반적이다.
- Keyword 필드에 문자열을 기대할 것이다.
- reindexing할 때 _source를 수정할 수 있다.
- 선택적으로 애플리케이션 레벨에서 처리될 수 있다.
reindexing할 때 _source값을 변경해보자.
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "reviews"
},
"dest": {
"index": "reviews_new"
},
"script": {
"source": """
if (ctx._source.product_id != null) {
ctx._source.product_id = ctx._source.product_id.toString();
}
"""
}
}Matching 쿼리를 사용하여 문서를 reindexing하기
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "reviews",
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "reviews_new"
}
}필드를 제거하고 reindexing하기
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "reviews",
"_source": ["content", "created_at", "rating"]
},
"dest": {
"index": "reviews_new"
}
}필드명 변경 (content -> comment)
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "reviews"
},
"dest": {
"index": "reviews_new"
},
"script": {
"source": """
ctx._source.comment = ctx._source.remove("content");
"""
}
}rating이 4.0이하는 무시하기
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "reviews"
},
"dest": {
"index": "reviews_new"
},
"script": {
"source": """
if (ctx._source.rating < 4.0) {
ctx.op = "noop"; # delete로 설정할 수도 있다.
}
"""
}
}script로 ctx.op 사용하기
- 일반적으로 query 파라미터 사용은 가능하다.
- 좀 더 폭넓은 경우에 ctx.op가 사용될 수 있다.
- query 파라미터를 사용하는 것이 성능상 더 좋다.
- "delete" 를 명시하면 대상 인덱스에서 문서를 삭제한다.
reindex API 파라미터
- 더 많은 파라미터가 사용될 수 있다.
- 예) version conflict 처리
- 문서를 reindexing하기 전에 snapshot이 생성된다.
- version conflict가 발생하면 기본적으로 취소된다.
- 대상 인덱스는 반드시 데이터가 있어야 한다.
batch & throttling
- reindex API는 batch로 동작한다.
- Update by query와 delete by query API와 같다.
- 내부적으로 scroll API를 사용한다.
- 수백만 건의 문서가 효과적으로 인덱싱될 수 있다.
- throttling은 성능에 영향도를 제한하기 위해 사용될 수 있다.
- 운영 cluster에 유용하다.
- 많은 문서를 reindex하려면 문서를 확인해라.
54. 필드 별칭(alias) 정의
필드 별칭(alias)
- 필드명은 문서를 reindexing할 때 변경될 수 있다.
- 대부분의 문서에서는 의미없는 일일 수도 있다.
- 필드 별칭을 사용하는 것은 선택사항이다.
- 문서를 reindex할 필요가 없다.
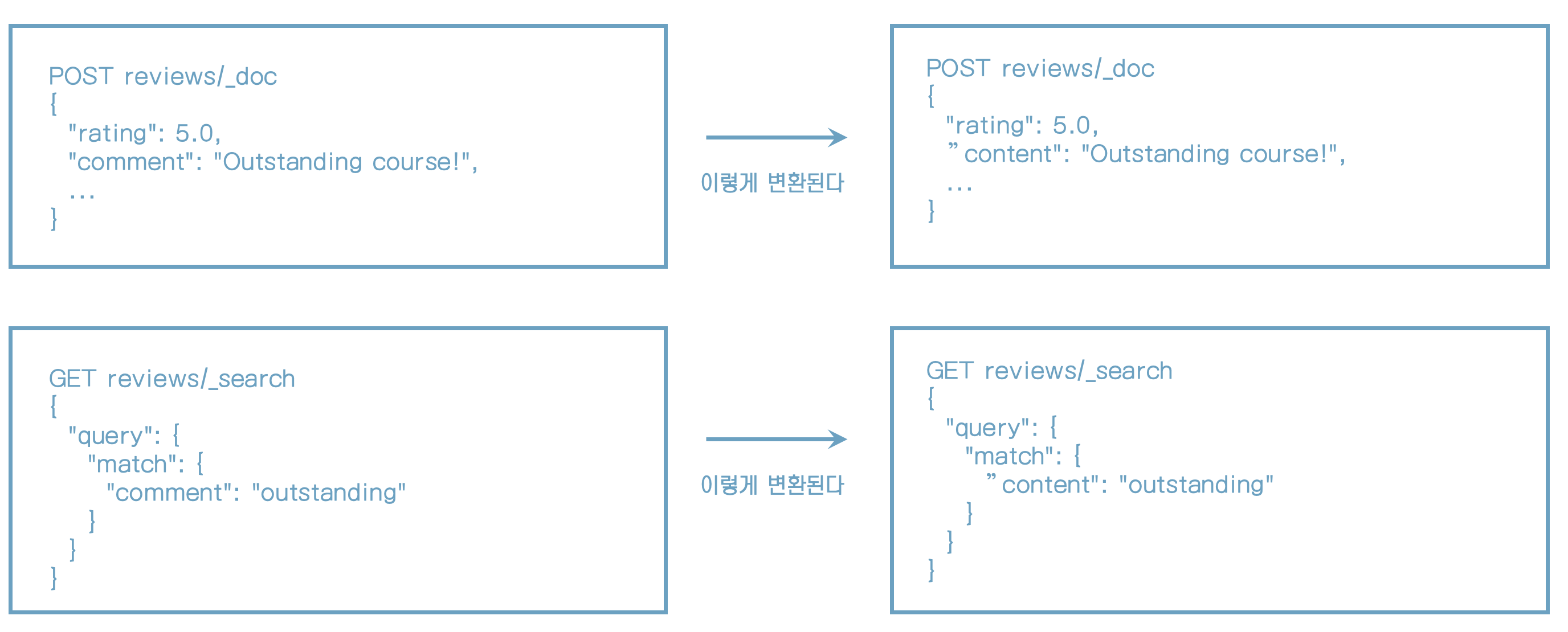
- comment를 content로 변경해보자.
- 별칭은 쿼리 내에서 사용될 수 있다.
- 별칭은 필드매핑을 정의된다.
content에 별칭으로 comment를 추가하자.
PUT reviews/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"comment": {
"type": "alias",
"path": "content"
}
}
}content로 검색하면 결과가 나온다.
GET reviews/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "outstanding"
}
}
}별칭으로 설정한 comment로 검색해도 결과가 나온다.
GET reviews/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"comment": "outstanding"
}
}
}필드 별칭 업데이트
- 필드 별칭은 실제로 업데이트 될 수 있다.
- 실제 대상 필드
- 단순히 새 path값으로 매핑 업데이트를 수행한다.
- 별칭은 인덱싱에 영향을 주지 않으므로 가능하다.
- Query 수준의 구성이다.
index 별칭
- 필드 별칭과 유사하게 elasticsearch는 index 별칭을 지원한다.
- 일반적으로 대용량을 처리할 때 사용된다.
55. multi 필드 매핑
PUT multi_field_test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"ingredients": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}ingredients에 text타입 외에 keyword 타입을 정의
POST multi_field_test/_doc
{
"description": "To make this spaghetti carbonara, you first need to...",
"ingredients": ["Spaghetti", "Bacon", "Eggs"]
}아래와 같이 검색해도 동일한 결과가 나온다.
GET multi_field_test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"ingredients": "Spaghetti"
}
}
}
GET multi_field_test/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"ingredients.keyword": "Spaghetti"
}
}
}56. index template
index template 소개
- index template은 settings와 mappings를 명시한다.
- 한개 이상의 패턴과 일치하는 인덱스에 적용된다.
- 패턴은 wildcard를 포함할 수 있다.
- index template은 새 인덱스를 만들 때 적용된다.
PUT _template/access-logs
{
"index_patterns": ["access-logs-*"],
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 2,
"index.mapping.coerce": false
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"@timestmap": {
"type": "date"
},
"url.original": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"http.request.referer": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"http.response.status.code": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}Index template을 정의했다.
새 인덱스를 만들자.
PUT access-logs-2020-01-01매핑 정보를 조회해보자.
GET access-logs-2020-01-01/_mappingindex pattern에서 만들 패턴으로 생성이 되었다.
{
"access-logs-2020-01-01" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"@timestmap" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"http" : {
"properties" : {
"request" : {
"properties" : {
"referer" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
},
"response" : {
"properties" : {
"status" : {
"properties" : {
"code" : {
"type" : "long"
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
"url" : {
"properties" : {
"original" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}index template의 우선순위
- 새 인덱스는 여러가지 index template에 해당될 수 있다.
- Order 파라미터가 index template의 우선순위를 정의하는데 사용될 수 있다.
- 값은 integer이다.
- 작은 값을 가진 template이 우선이다.
index template 수정하기
PUT _template/access-logsindex template 조회하기
GET _template/access-logsindex template 삭제하기
DELETE _template/access-logs57. Elastic Common Schema(ECS) 소개
ECS는 무엇인가?
- 공통 필드에 대한 명세이고 어떻게 매핑되는가
- ECS 전에필드 이름간 연결이 없었다.
- nginx에서 로그를 취합하는 것은 apache와 다른 이름을 사용할 것이다.
- ECS는 동일한 것에 대한 공통 필드를 의미한다.
- 예) @timestamp
- 사용 케이스와 무관하다.
- 필드 그룹은 필드 셋을 의미한다.
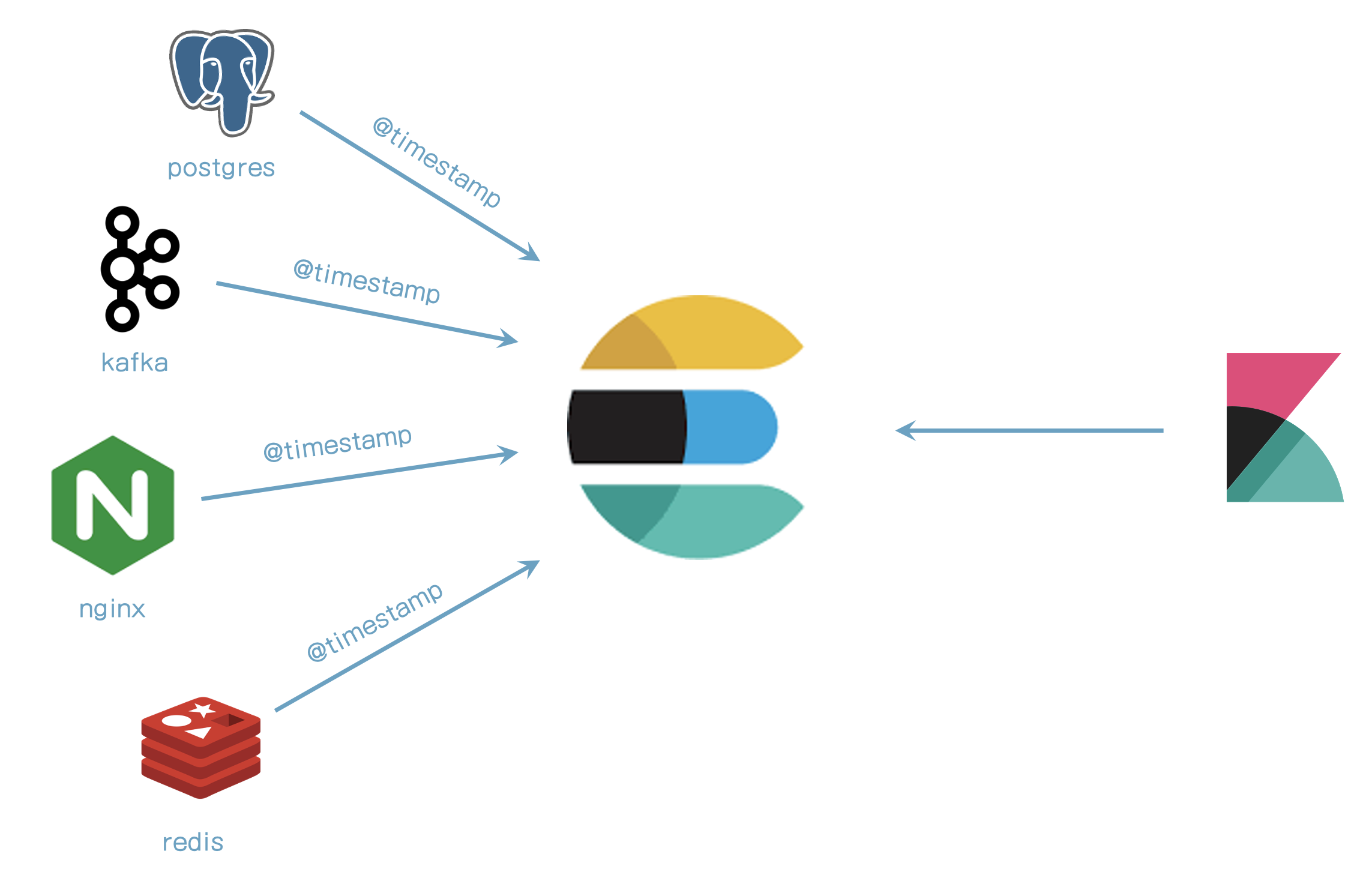
ECS의 사용
- ECS에서 문서는 이벤트를 의미한다.
- ECS는 이벤트가 아닌 필드를 사용할 수 없다.
- 주로 표준 이벤트에 유용하다.
- 예) 웹서버 로그, 운영체제 지표 등
- ECS는 자동으로 elastic stack 제품군에서 처리된다.
- 만일 elastic stack을 사용한다면 ECS를 설정할 필요가 없다.
- ECS를 사용할 필요가 없지만 무엇인지 알 필요는 있다.
58. 동적(dynamic) 매핑 소개
POST my-index/_doc
{
"tags": ["computer", "electronics"],
"in_stock": 4,
"created_at": "2020/01/01 00:00:00"
}문서를 추가하면 아래 처럼 자동으로 매핑이 생긴다.
{
"my-index" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"created_at" : {
"type" : "date",
"format" : "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy/MM/dd||epoch_millis"
},
"in_stock" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"tags" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}| JSON | ELASTICSEARCH |
|---|---|
| string | 다음 중 하나 keyword 매핑을 가진 text 필드 date 필드 (float 혹은 long 필드) |
| integer | long |
| floating point number | float |
| boolean | boolean |
| object | object |
| Array | 첫번째 값이 non-null인지에 따라 |
59. 명시적인 매핑과 동적 매핑 연결
first_name은 text타입으로 매핑하고 last_name은 동적매핑으로 추가하면 어떻게 구성될까?
first_name 매핑 추가
PUT people
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"first_name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}last_name 필드 추가
POST people/_doc
{
"first_name": "Bo",
"last_name": "Andersen"
}people 조회
GET people/_mappingfirst_name은 text로 매핑되지만 last_name은 text와 keyword로 매핑된다.
{
"people" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"first_name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"last_name" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}60. 동적 매핑 구성하기
PUT people
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": false,
"properties": {
"first_name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
POST people/_doc
{
"first_name": "Bo",
"last_name": "Andersen"
}매핑을 조회하면
GET people/_mappingfirst_name만 매핑으로 연결되어 있다.
{
"people" : {
"mappings" : {
"dynamic" : "false",
"properties" : {
"first_name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}데이터를 조회하면 데이터는 입력되어 있다.
GET people/_searchdynamic을 false로 설정
- 새 필드가 무시된다.
- 인덱싱이 되지 않지만 _source에는 여전히 표시된다.
- last_name 필드에 역색인파일이 생성이 되지 않는다.
- 필드 조회를 하면 결과가 나오지 않는다.
- 필드는 매핑없이 인덱싱되지 않는다.
- enabled될 때 값을 인덱싱하기 전에 동적 매핑을 생성한다.
- 새 필드는 명시적인 매핑되어야 한다.
더 좋은 방법
- dynamic을 strict으로 설정
- Elsticsearch는 매핑되지 않은 필드를 무시한다.
- 모든 필드는 명시적으로 매핑되어야 한다.
- 관계형 DB와 유사
PUT people
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"first_name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}매핑되지 않은 값을 입력하면
POST people/_doc
{
"first_name": "Bo",
"last_name": "Andersen"
}오류가 발생한다.
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason" : "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [last_name] within [_doc] is not allowed"
}
],
"type" : "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason" : "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [last_name] within [_doc] is not allowed"
},
"status" : 400
}61. 동적 template
매핑을 정의
PUT dynamic_template_test
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"integers": {
"match_mapping_type": "long",
"mapping": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
]
}
}데이터 추가
POST dynamic_template_test/_doc
{
"in_stock": 123
}데이터 조회
GET dynamic_template_test/_mapping62. 매핑 권장사항
명시적인 매핑을 사용하라.
- 동적 매핑은 편하지만 운영에서는 좋은 방법이 아니다.
- 많은 문서를 저장할 때 디스크 공간을 절약하라
- dynamic을 false가 아닌 strict로 설정하라.
- 기대하지 않은 결과를 없애준다.
text 필드 매핑
- string을 text와 keyword 둘다 매핑하지 마라.
- 일반적으로 하나만 필요하다.
- 각 매핑은 디스크 공간을 필요로 한다.
- Full-text 검색이 필요한가?
- Text 매핑을 추가하라
- 집합, 정렬, 필터링이 필요한가?
- keyword를 사용하라.
coercion을 비활성화해라
- coercion은 잘못될 일이 발생할 수 있다.
- 의도한 대로 하도록 노력해라.
- 가능하면 올바른 데이터 타입을 사용해라.
적절한 numeric 데이터 타입을 사용하라.
- 일반적인 숫자에서는 integer 데이터 타입이면 충분하다.
- long은 큰 숫자를 저장할 수 있지만 많은 디스크 공간을 사용한다.
- decimal 숫자에서는 float 데이터 타입이면 충분하다.
- double은 좀 더 정확하지만 디스크 공간을 2배 사용한다.
- 보통 float이면 충분하다.
매핑 파라미터
- 정렬, 집합, 스크립팅이 필요없다면 doc_values를 false로 설정하라.
- scoring이 필요없다면 norms를 false로 설정하라.
- 값을 필터링할 필요 없다면 index를 false로 설정하라.
- 여전히 집합(aggregation)을 사용할 수 있다.
63. stemming & stop words
)
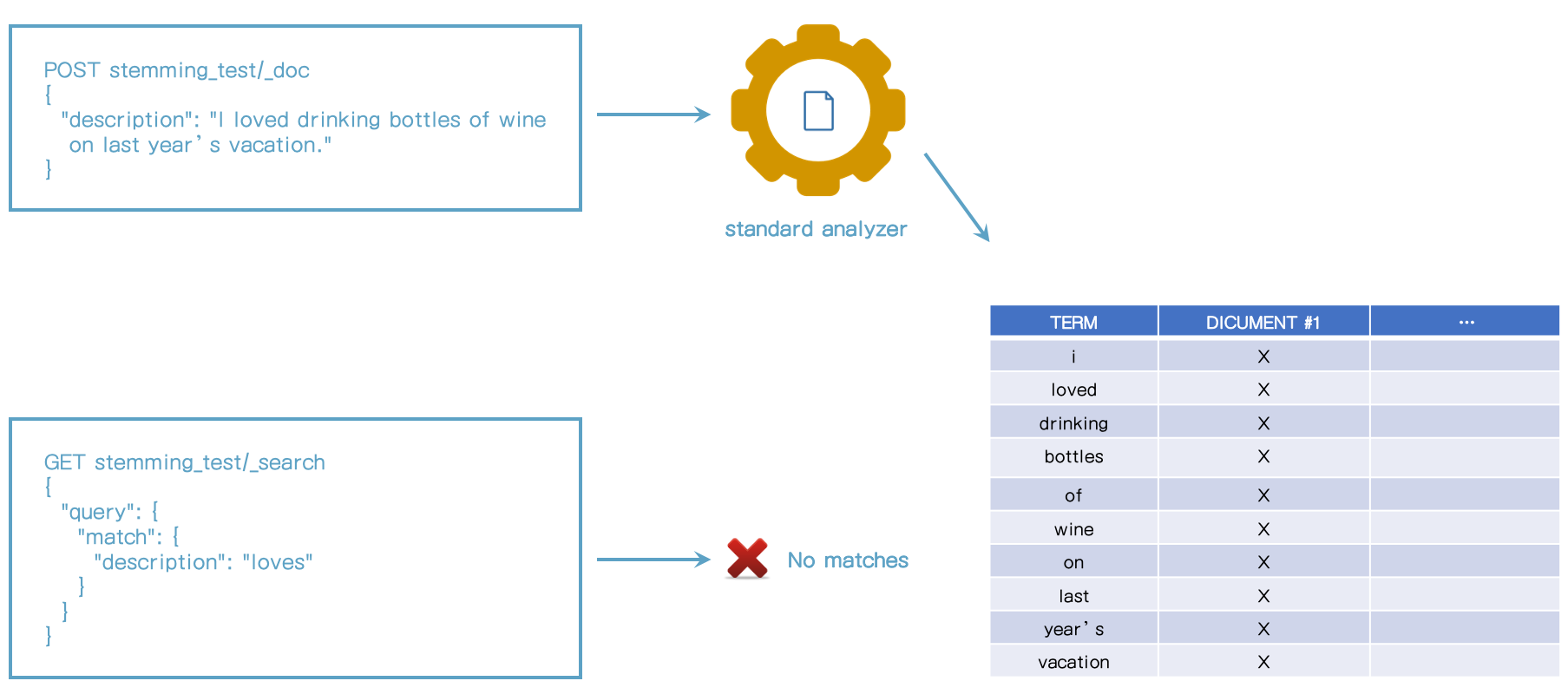
stemming 소개
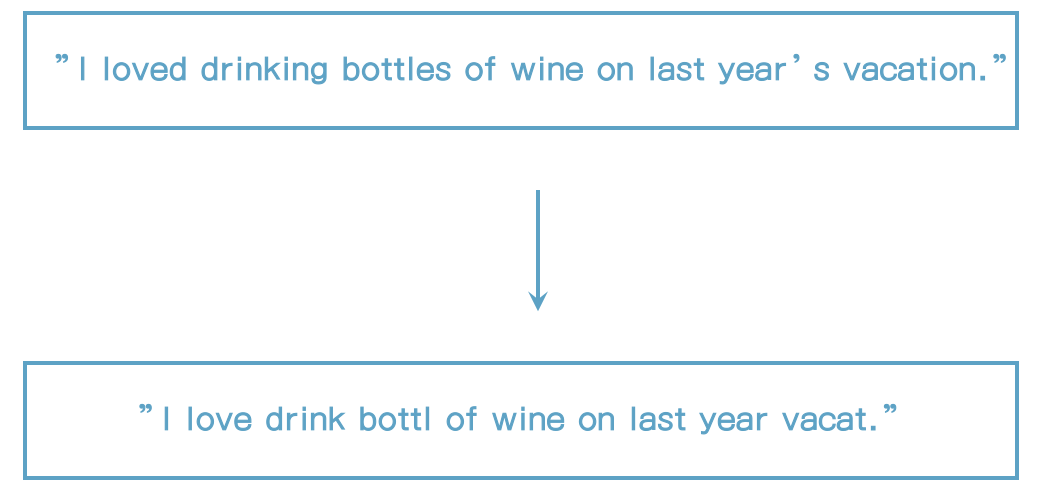
- stemming은 단어들을 기본형으로 줄여준다.
- 예) loved -> love, drinking -> drink
- 모든 단어를 올바르게 줄이지는 못한다.
stop words 소개
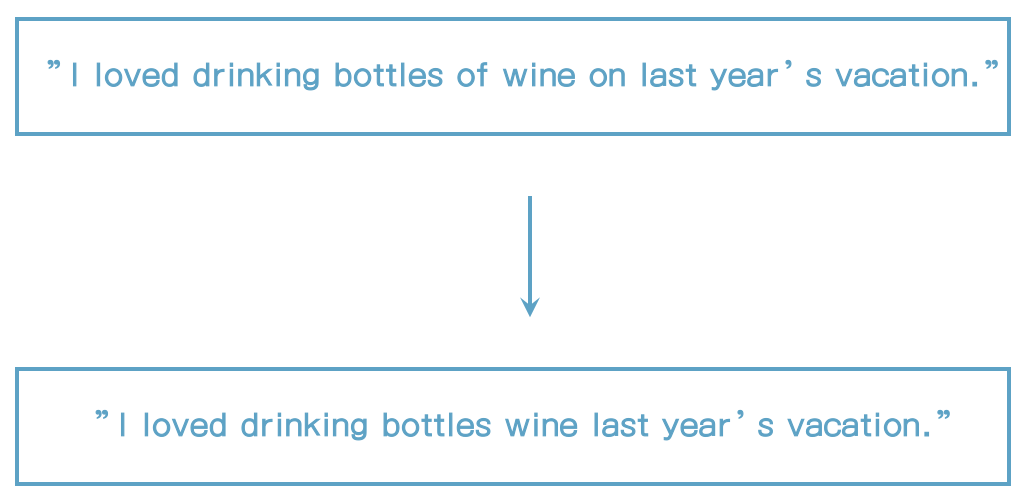
- Text 분석에 필터링 되어야 할 단어들
- "a", "the", "at", "of", "on" 등과 같은 일반적인 단어들
- 이런 단어들은 scoring할 때 크게 의미 없다.
- 특정 단어를 없앨 때 사용
- 과거보다는 현재 elasticsearch에서 덜 사용한다.
- Relevance 알고리즘이 많이 좋아졌다.
- 과거보다는 현재 elasticsearch에서 덜 사용한다.
- 기본은 제거되지 않고 일반적으로 권장되지 않는다.
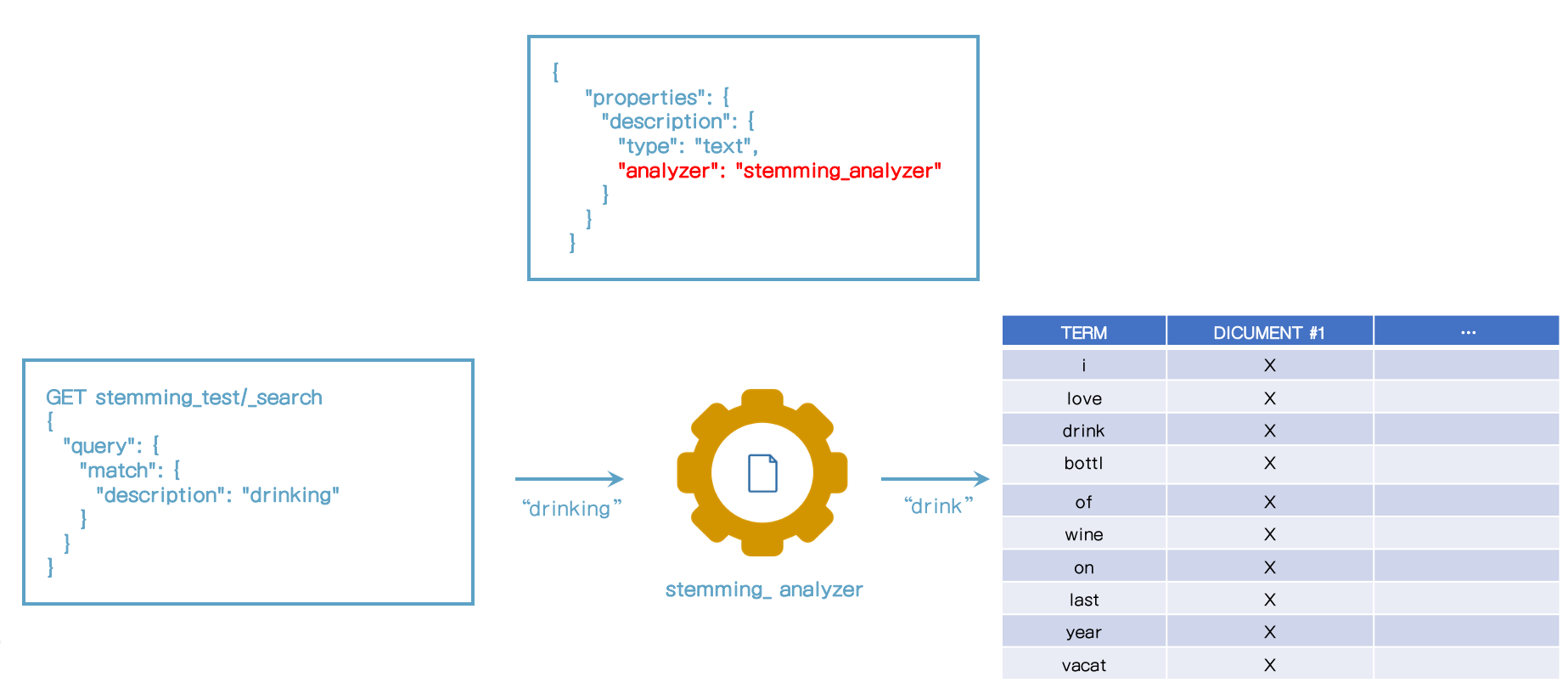
64. Analyzer와 검색 쿼리
65. 내장 analyzer
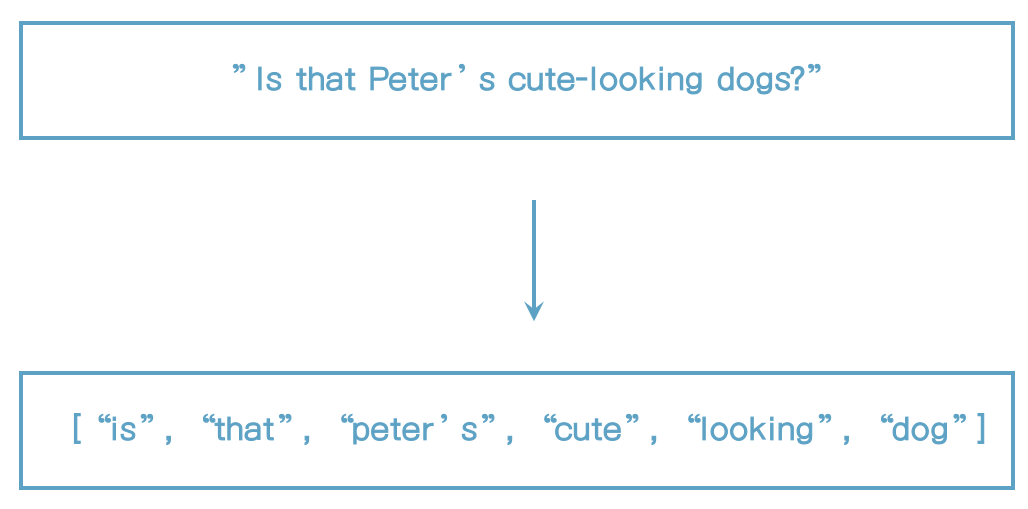
standard analyer
- text를 단어 단위로 짜르고 구두점을 제거한다.
- standard tokenizer
- lowercase token filter로 문자를 소문자로 바꾼다.
- stop token filter를 포함 (기본은 비활성화)
예제
simple analyzer
- standard analyzer와 유사
- 문자 외에 다른 단어를 만나면 토큰으로 구분
- 문자를 lowercase tokenizer로 소문자로 변환
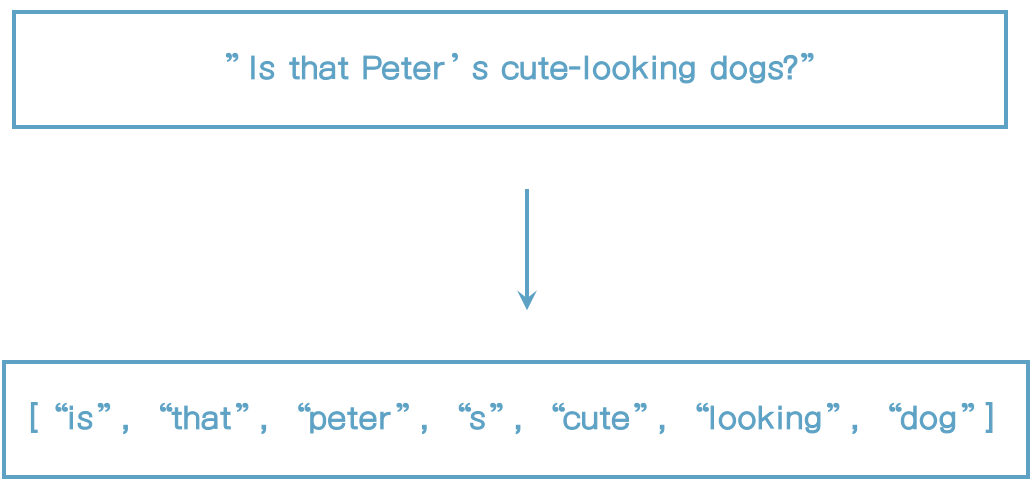
whitespace analyzer
- 공백으로 토큰을 분리
- 문자를 소문자로 바꾸지 않는다.
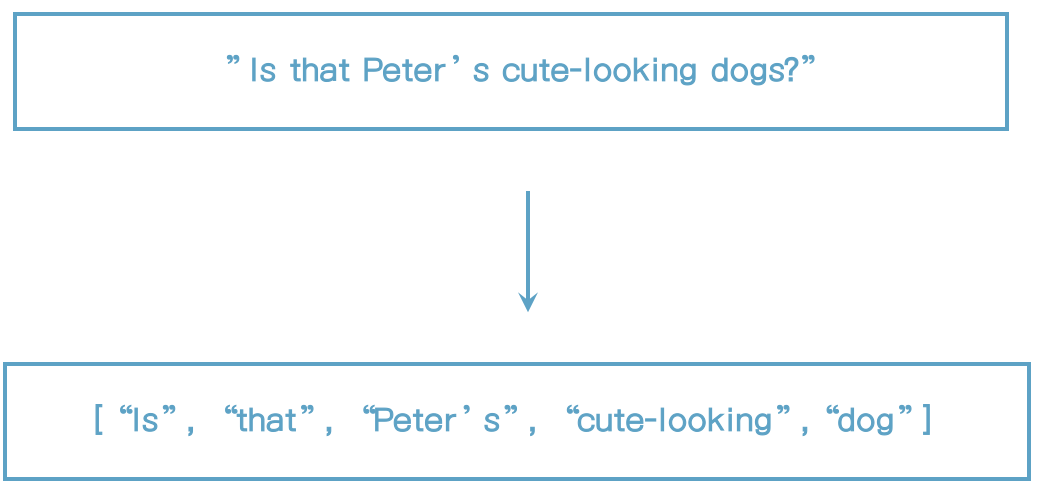
keyword analyzer
- 입력 text를 그대로
- 하나의 토큰으로 사용
- Keyword 필드에 기본으로 사용
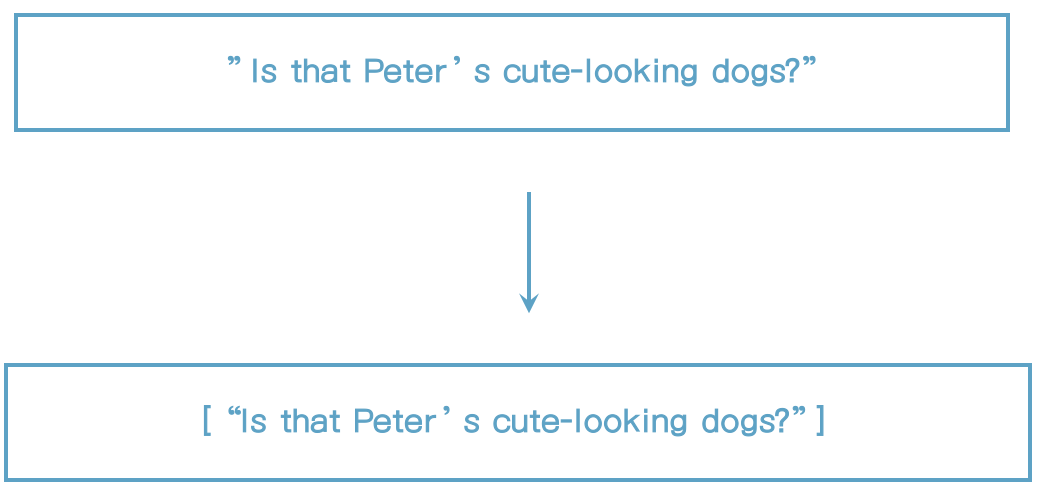
pattern analyzer
- 토큰을 분리하기 위해 정규 표현식이 사용된다.
- 일치하는 text를 토큰으로 구분한다.
- 이 analyzer는 유연하게 사용할 수 있다.
- 기본 패턴을 단어가 글자이다. (\W+)
- 소문자가 기본이다.
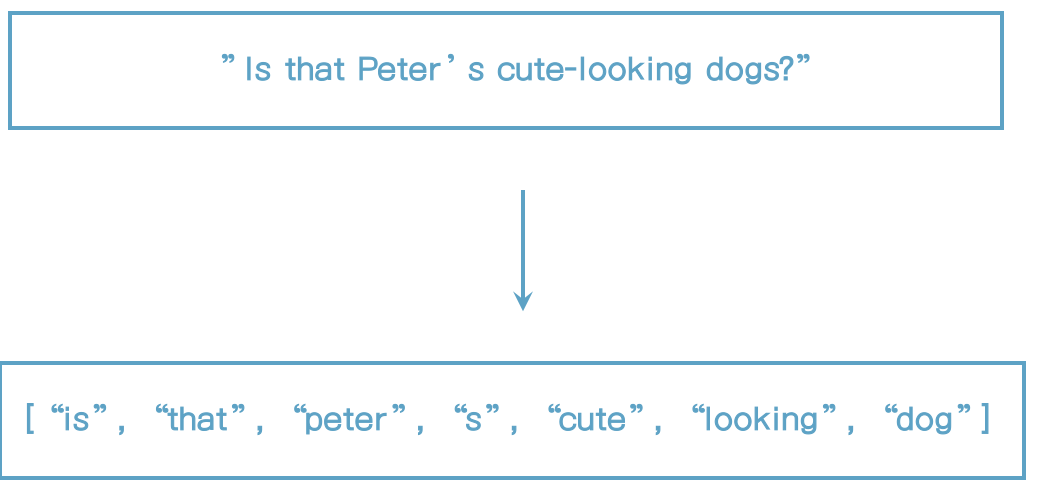
english analyzer
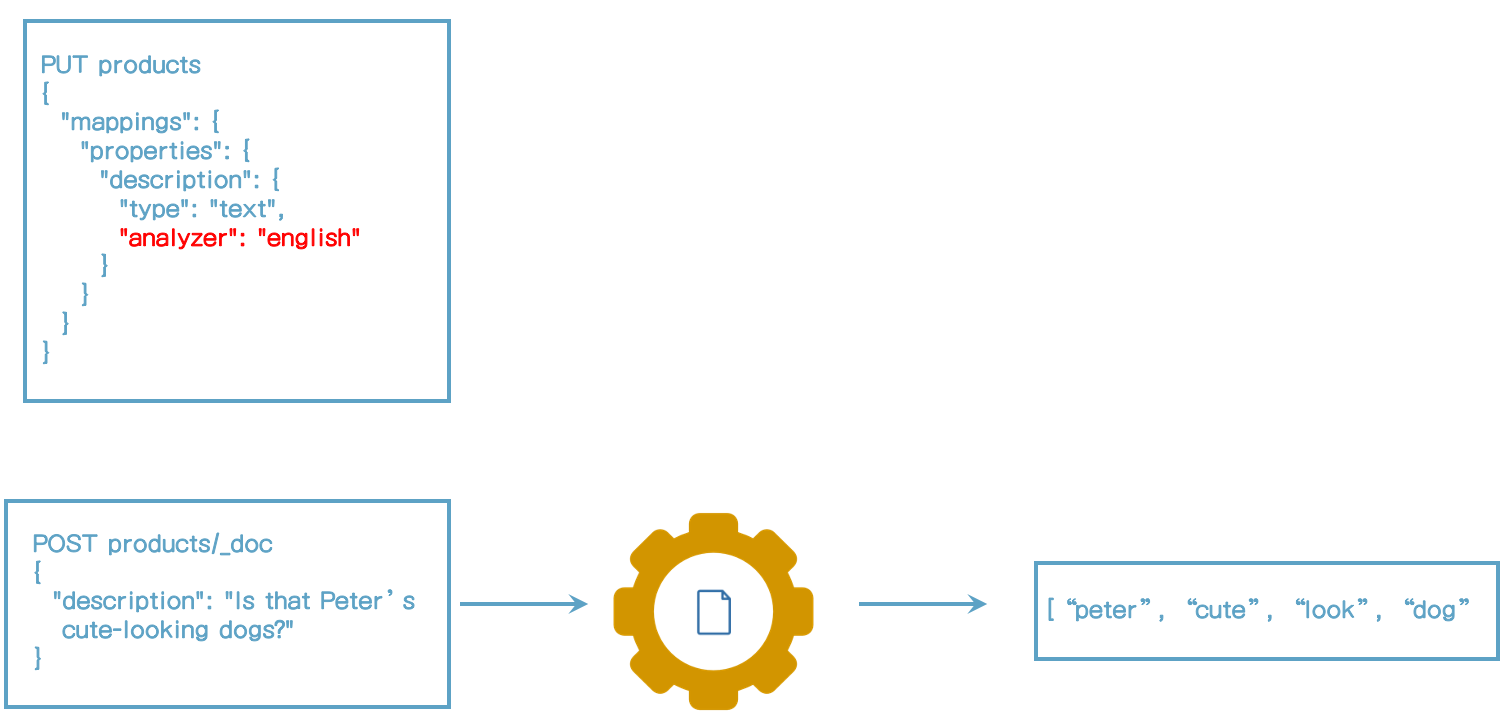
내장 analyzer 구성하기
PUT products
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"remove_english_stop_words": {
"type": "standard",
"stopwords": "_english_"
}
}
}
}
}68. custom analyzer 생성
PUT analyzer_test
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_custom_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": ["html_strip"],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
"stop",
"asciifolding"
]
}
}
}
}
}POST analyzer_test/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "my_custom_analyzer",
"text": "I'm in a <em>good</em> mood - and I <strong>love</strong> açaí!"
}결과는 다음과 같다.
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "i'm",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "good",
"start_offset" : 18,
"end_offset" : 27,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "mood",
"start_offset" : 28,
"end_offset" : 32,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "i",
"start_offset" : 49,
"end_offset" : 50,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "love",
"start_offset" : 59,
"end_offset" : 72,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "acai",
"start_offset" : 73,
"end_offset" : 77,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 8
}
]
}69. 기존 인덱스에 analyzer 추가
위에서 만든 custom_analyer를 변경하자.
PUT analyzer_test/_settings
{
"analysis": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_second_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": ["html_strip"],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
"stop",
"asciifolding"
]
}
}
}
}
}실행하면 아래와 같은 오류가 발생한다.
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "Can't update non dynamic settings [[index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.char_filter, index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.type, index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.tokenizer, index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.filter]] for open indices [[analyzer_test/iINbtwEpRW6k9TXwQDEoVA]]"
}
],
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "Can't update non dynamic settings [[index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.char_filter, index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.type, index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.tokenizer, index.analysis.analysis.analyzer.my_second_analyzer.filter]] for open indices [[analyzer_test/iINbtwEpRW6k9TXwQDEoVA]]"
},
"status" : 400
}open & closed 인덱스
- Open 인덱스는 인덱싱하고 조회할 때 사용할 수 있다.
- Closed 인덱스는 요청을 거부한다.
- 읽기/쓰기 요청이 거부된다.
- 특정 동작을 수행할 때 필요하다.
dynamic, static settings
- dynamic settings는 인덱스를 close하지 않고 변경될 수 있다.
- 다운타임이 필요 없다.
- static settings는 인덱스를 먼저 closed해야 한다.
- 인덱스는 사용할 수 없다.
- Analysis settings는 static settings이다.
analyzer_test를 close해보자.
POST analyzer_test/_close다시 custom_analyzer를 변경하자.
PUT analyzer_test/_settings
{
"analysis": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_second_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": ["html_strip"],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
"lowercase",
"stop",
"asciifolding"
]
}
}
}
}
}인덱스를 open하자.
POST analyzer_test/_open_settings를 조회하면 analyzer가 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
GET analyzer_test/_settings인덱스 open/close
- 빠르지만 운영 클러스터에서는 사용해서는 안된다.
- 예) 다운타임이 있으면 안되는 중요 업무
- 선택적으로 문서를 새 인덱스로 reindex할 때
- 새로운 setting정보로 인덱스를 생성할 때
- 인덱스 별칭(alias)을 사용
70. Analyzer 수정하기
my_custom_analyzer 추가
PUT analyzer_test/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"description": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "my_custom_analyzer"
}
}
}문서 추가
POST /analyzer_test/_doc
{
"description": "Is that Peter's cute-looking dog?"
}문서 조회
GET analyzer_test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": {
"query": "that",
"analyzer": "keyword"
}
}
}
}결과가 나오지 않는다.
그 이유는 analyzer에 stop 필터가 추가되어서 that이 제거되었기 때문이다.
해당 analyzer를 변경해보자.
우선 인덱스를 close 하자
POST analyzer_test/_close그리고 나서 anaylzer를 변경하자.
PUT analyzer_test/_settings
{
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_custom_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": ["html_strip"],
"filter": [
"lowercase",
"asciifolding"
]
}
}
}
}다시 인덱스를 open을 하자.
POST analyzer_test/_opensetting을 조회해보면 변경됬음을 확인할 수 있다.
GET analyzer_test/_settings결과
{
"analyzer_test" : {
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"routing" : {
"allocation" : {
"include" : {
"_tier_preference" : "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards" : "1",
"provided_name" : "analyzer_test",
"creation_date" : "1662965220554",
"analysis" : {
"analyzer" : {
"my_custom_analyzer" : {
"filter" : [
"lowercase",
"asciifolding"
],
"char_filter" : [
"html_strip"
],
"type" : "custom",
"tokenizer" : "standard"
}
}
},
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "0WZ0Nxc6T2yvcUlIGHHCGA",
"version" : {
"created" : "7110099"
}
}
}
}
}데이터를 1건 더 입력해보자.
POST analyzer_test/_doc
{
"description": "Is that Peter's cute-looking dog?"
}다시 조회를 해보면
GET analyzer_test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": {
"query": "that",
"analyzer": "keyword"
}
}
}
}1건이 나오는 것을 알 수 있다.
하지만 이전에 입력했던 데이터는 나오지 않는다.
2가지 유형의 analyzer가 동시에 사용되고 있음을 알 수 있다. (첫 번째는 stop 필터가 적용, 두번째는 stop필터가 적용되지 않은 버전)
analyzer_test를 조회해보면 2가지 데이터가 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
GET analyzer_test/_search결과
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "analyzer_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "rKN1MIMB72KeG_cXOvn6",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"description" : "Is that Peter's cute-looking dog?"
}
},
{
"_index" : "analyzer_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "raN6MIMB72KeG_cXnPlw",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"description" : "Is that Peter's cute-looking dog?"
}
}
]
}
}정상적으로 조회하기 위해서 해당 인덱스를 새 인덱스로 생성해야 할 필요가 있다.
좀 더 간단한 방법으로 Update By Query를 사용할 수 있다.
아래 쿼리를 실행해보자.
POST analyzer_test/_update_by_query?conflicts=proceed그런 다음 다시 조회해보자.
GET analyzer_test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": {
"query": "that",
"analyzer": "keyword"
}
}
}
}결과
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.13353139,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "analyzer_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "rKN1MIMB72KeG_cXOvn6",
"_score" : 0.13353139,
"_source" : {
"description" : "Is that Peter's cute-looking dog?"
}
},
{
"_index" : "analyzer_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "raN6MIMB72KeG_cXnPlw",
"_score" : 0.13353139,
"_source" : {
"description" : "Is that Peter's cute-looking dog?"
}
}
]
}
}결과가 2건이 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.

